PROBLEMS
Question 39.1
1. Minimal code. What is the minimum number of contiguous bases required to encode 20 amino acids? Explain your answer. ✓ 1
Question 39.2
2. Nearly universal. Why has the code remained nearly invariant through billions of years of evolution, from bacteria to human beings? ✓ 1
Question 39.3
3. Like Pooh and Christopher Robin. Match each term with its description.
Translation Genetic code Codon tRNA Anticodon loop Wobble Aminoacyl- Ribosome 50S subunit 30S subunit | Protein synthesis Contains 16S RNA Interacts with the codon Three nucleotides Site of protein synthesis Nucleic acid information to protein information Carrier of activated amino acids Code reader Pairing freedom Contains 28S and 5S RNA |
Question 39.4
4. A code you can live by. What are the key characteristics of the genetic code? ✓ 1
Question 39.5
5. Degeneracy. Usually degeneracy should be avoided, except perhaps in well-
Question 39.6
6. Odds of getting it right. Calculate the probability of synthesizing an error-
Question 39.7
7. Careful, but not too careful. Why is it crucial that protein synthesis has an error frequency of 10−4?
Question 39.8
8. Going wobbly. Explain how it is possible that some tRNA molecules recognize more than one codon. ✓ 1
Question 39.9
9. Encoded sequences.
(a) Write the sequence of the mRNA molecule synthesized from a DNA template strand having the following sequence. ✓ 1
5′-ATCGTACCGTTA-
(b) What amino acid sequence is encoded by the following base sequence of an mRNA molecule? Assume that the reading frame starts at the 5′ end.
5′-UUGCCUAGUGAUUGGAUG-
(c) What is the sequence of the polypeptide formed on addition of poly(UUAC) to a cell-
Question 39.10
10. Deciphering the code, 1. Synthetic RNA molecules of defined sequence were instrumental in deciphering the genetic code. Their synthesis first required the synthesis of DNA molecules to serve as a template. H. Gobind Khorana synthesized, by organic-
Question 39.11
11. Deciphering the code, 2. The code word GGG cannot be deciphered in the same way as can UUU, CCC, and AAA, because poly(G) does not act as a template for protein synthesis. Poly(G) forms a triple-
Question 39.12
12. Overlapping or not. In a nonoverlapping triplet code, each group of three bases in a sequence ABCDEF … specifies only one amino acid—
Question 39.13
13. Triple entendre. The RNA transcript of a region of T4 phage DNA contains the sequence 5′-AAAUGAGGA-
Question 39.14
14. Valuable synonyms. Proteins generally have low contents of Met and Trp, intermediate ones of His and Cys, and high ones of Leu and Ser. What does this observation suggest about the relation between the number of codons of an amino acid and its frequency of occurrence in proteins? What might be the selective advantage of this relation?
Question 39.15
15. A new translation. A transfer RNA with a UGU anticodon is enzymatically conjugated to 14C-
5′-UUUUGCCAUGUUUGUGCU-
What is the sequence of the corresponding radiolabeled peptide?
Question 39.16
16. Commonalities. What features are common to all tRNA molecules? ✓ 2
Question 39.17
17. The ol’ two step. What two reaction steps are required for the formation of an aminoacyl-
Question 39.18
18. The same but different. Why must tRNA molecules have both unique structural features and common structural features? ✓ 2
Question 39.19
19. Charge it. In the context of protein synthesis, what is meant by an activated amino acid? ✓ 2
Question 39.20
20. 1 = 2, for sufficiently large values of 1. The energetic equivalent of two molecules of ATP is used to activate an amino acid, yet only one molecule of ATP is used. Explain.
Question 39.21
21. Sieves. Using threonyl-
Question 39.22
22. Knowledge rich. Aminoacyl-
Challenge Problems
Question 39.23
23. A tougher strand. RNA is readily hydrolyzed by alkali, whereas DNA is not. Why?
Question 39.24
24. Synthetase mechanism. The formation of isoleucyltRNA proceeds through the reversible formation of an enzyme-
(a) ATP and 32PPi
(b) tRNA, ATP, and 32PPi
(c) Isoleucine, ATP, and 32PPi
Question 39.25
25. Finding direction. A series of experiments were performed to establish the direction of chain growth in protein synthesis. Reticulocytes (young red blood cells) that were actively synthesizing hemoglobin were treated with [3H]leucine. In a period of time shorter than that required to synthesize a complete chain, samples of hemoglobin were taken, separated into α and β chains, and analyzed for the distribution of 3H within their sequences. In the earliest samples, only regions near the carboxyl ends contained radioactivity. In later samples, radioactivity was present closer to the amino terminus as well. Explain how these results determine the direction of chain growth in protein synthesis.
Question 39.26
26. Mission possible. Your mission, should you accept it, is to determine the direction in which the mRNA is read during protein synthesis. You are provided with synthetic polynucleotide
as the template in a cell-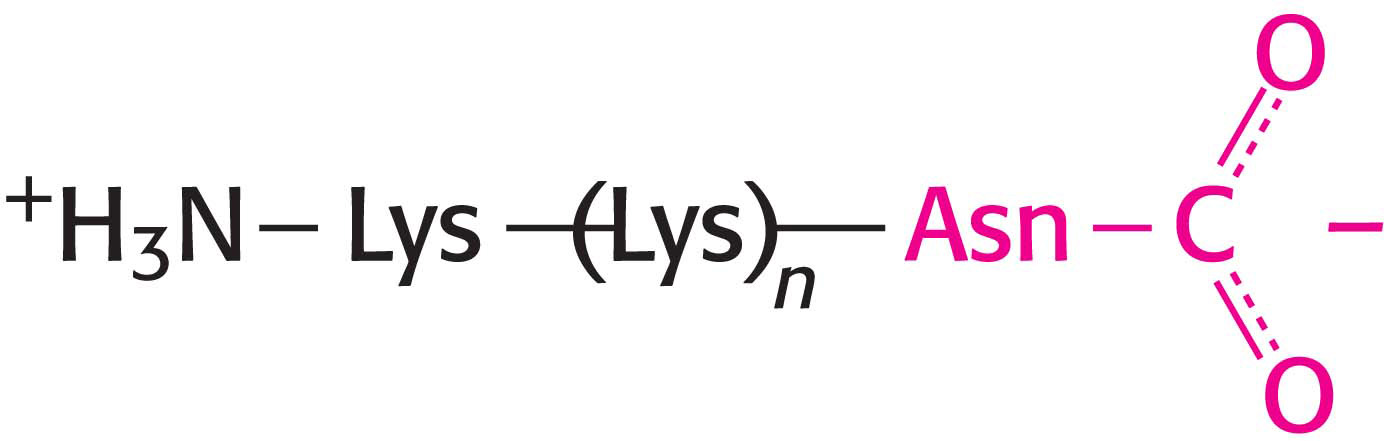
What does the nature of this product say about the direction in which the mRNA is read? ✓ 2
Selected Readings for this chapter can be found online at www.whfreeman.com/