PROBLEMS
Question 41.1
1. Building a library. What is a cDNA library? How it is constructed? ✓ 8
Question 41.2
2. Different libraries. Differentiate between a cDNA library and a genomic library. ✓ 8
Question 41.3
3. It’s not the heat, … Why is Taq polymerase especially useful for PCR? ✓ 8
Question 41.4
4. Like Marie and Pierre. Match each term with its description. ✓ 8
cDNA library Reverse transcriptase Restriction enzyme Vector Sticky ends DNA ligase Genomic library Sanger dideoxy method Polymerase chain reaction DNA microarray | Measures the expression of many genes Complementary single strands of DNA DNA sequences representing mRNA Cleave double- Copies RNA into DNA Piece of DNA taken up and replicated by bacteria Sequencing by strand termination Fragments of DNA, housed in phages, that represent an entire genome Joins two DNA molecules Amplifies selected DNA sequences |
Question 41.5
5. Probe design. Which of the following amino acid sequences would yield the most optimal oligonucleotide probe? ✓ 8
Question 41.6
6. The right template. Ovalbumin is the major protein of egg white. The chicken ovalbumin gene contains eight exons separated by seven introns. Which should be used to form the protein in E. coli: ovalbumin cDNA or ovalbumin genomic DNA? Why?
Question 41.7
7. Cleavage frequency. The restriction enzyme AluI cleaves at the sequence 5′-AGCT-
Question 41.8
8. The right cuts. Suppose that a human genomic library is prepared by exhaustive digestion of human DNA with the EcoRI restriction enzyme. Fragments averaging about 4 kb in length will be generated. Is this procedure suitable for cloning large genes? Why or why not? ✓ 8
Question 41.9
9. Reading sequences. An autoradiogram of a sequencing gel containing four lanes of DNA fragments is shown in the adjoining illustration. ✓ 8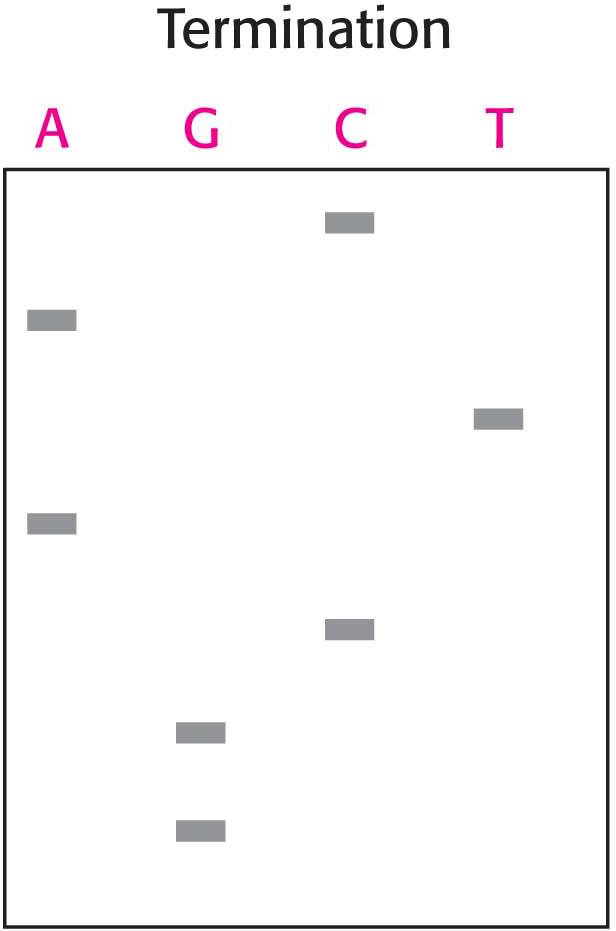
(a) What is the sequence of the DNA fragment?
(b) Suppose that the Sanger dideoxy method shows that the template-
Question 41.10
10. A revealing cleavage. Sickle-
Question 41.11
11. A blessing and a curse. The power of PCR can create problems. Suppose someone claims to have isolated dinosaur DNA by using PCR. What questions might you ask to determine if it is indeed dinosaur DNA? ✓ 8
Question 41.12
12. Questions of accuracy. The stringency of PCR amplification can be controlled by altering the temperature at which the primers and the target DNA undergo hybridization. How would altering the temperature of hybridization affect the amplification? Suppose that you have a particular yeast gene A and that you wish to see if it has a counterpart in human beings. How would controlling the stringency of the hybridization help you? ✓ 8
Question 41.13
13. A puzzling ladder. A gel pattern displaying PCR products shows four strong bands. The four pieces of DNA have lengths that are approximately in the ratio of 1:2:3:4. The largest band is cut out of the gel, and PCR is repeated with the same primers. Again, a ladder of four bands is evident in the gel. What does this result reveal about the structure of the encoded protein?
Question 41.14
14. Man’s best friend. Why might the genomic analyses of dogs be particularly useful for investigating the genes responsible for body size and other physical characteristics?
Chapter Integration Problem
Question 41.15
15. Designing primers. A successful PCR experiment often depends on designing the correct primers. In particular, the Tm, the melting temperature of a double helix, for each primer should be approximately the same. What is the basis of this requirement? ✓ 8
Data Interpretation Problems
Question 41.16
16. DNA diagnostics. Representations of sequencing gels for variants of the α chain of human hemoglobin are shown here. What is the nature of the amino acid change in each of the variants? The first triplet encodes valine.
Question 41.17
17. Two peaks. In the course of studying a gene and its possible mutation in humans, you obtain genomic DNA samples from a collection of persons and PCR amplify a region of interest within this gene. For one of the samples, you obtain the sequencing chromatogram shown here. Explain the appearance of these data at position 49 (indicated by the arrow).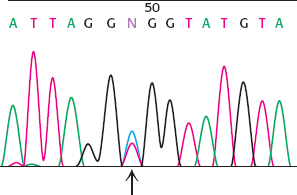
Question 41.18
18. Any direction but east. A series of people are found to have difficulty eliminating certain types of drugs from their bloodstreams. The problem has been linked to a gene X, which encodes an enzyme Y. Six people were tested with the use of various techniques of molecular biology. Person A is a normal control, person B is asymptomatic but some of his children have the metabolic problem, and persons C through F display the trait. Tissue samples from each person were obtained. Southern analysis was performed on the DNA after digestion with the restriction enzyme HindIII. Northern analysis of mRNA also was done. In both types of analysis, the gels were probed with labeled X cDNA. Finally, a western blot with an enzyme-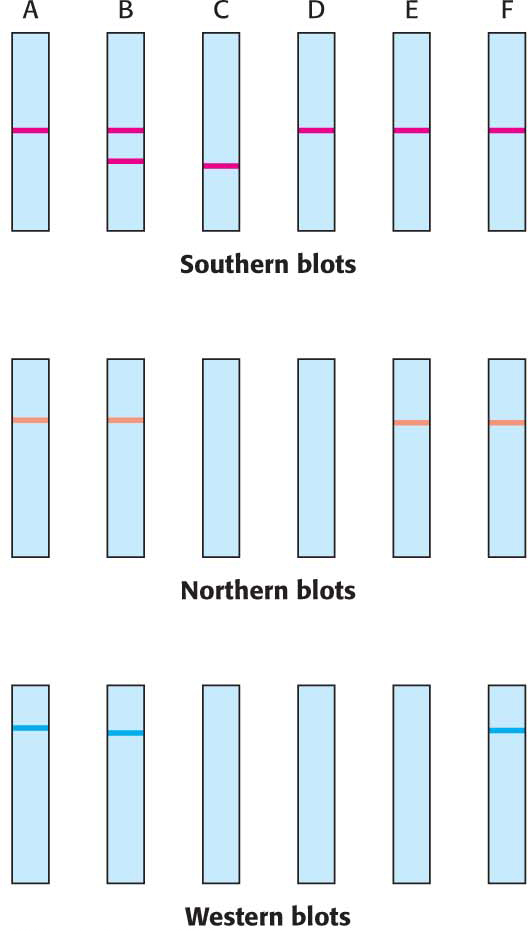
Challenge Problems
Question 41.19
19. Many melodies from one cassette. Suppose that you have isolated an enzyme that digests paper pulp and have obtained its cDNA. The goal is to produce a mutant that is effective at high temperature. You have engineered a pair of unique restriction sites in the cDNA that flank a 30-
Question 41.20
20. Terra incognita. PCR is typically used to amplify DNA that lies between two known sequences. Suppose that you want to explore DNA on both sides of a single known sequence. Devise a variation of the usual PCR protocol that would enable you to amplify entirely new genomic terrain. ✓ 8
Question 41.21
21. Chromosome walking. Propose a method for isolating a DNA fragment that is adjacent in the genome to a previously isolated DNA fragment. Assume that you have access to a complete library of DNA fragments in a vector but that the sequence of the genome under study has not yet been determined. ✓ 8
Selected Readings for this chapter can be found online at www.whfreeman.com/