
7.1 Kinetics Is the Study of Reaction Rates
✓ 3 Explain what reaction velocity is.
The study of the rates of chemical reactions is called kinetics, and the study of the rates of enzyme-
What do we mean when we say the “velocity” or “rate” of a chemical reaction? Consider a simple reaction:

The velocity of the reaction, V (for velocity), is the quantity of reactant A that disappears in a specified unit of time t. It is equal to the velocity of the appearance of product P, or the quantity of P that appears in a specified unit of time:
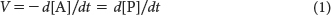
where d is the decrease in substrate concentration or the increase in product concentration. If A is yellow and P is colorless, we can follow the decrease in the concentration of A by measuring the decrease in the intensity of yellow color with time. Consider only the change in the concentration of A for now. The velocity of the reaction is directly related to the concentration of A by a proportionality constant k, called the rate constant:

Reactions in which the velocity is directly proportional to the reactant concentration are called first-
Many important biochemical reactions are biomolecular; that is, they include two reactants. Such reactions are called second-

or

The corresponding rate equations often take the form

and

The rate constants, called second-
Sometimes, second-
Interestingly enough, under some conditions, a reaction can be zero order. In these cases, the rate is independent of reactant concentrations. As we will see shortly, enzyme-