SUMMARY
7.1 Kinetics Is the Study of Reaction Rates
The velocity of a reaction is determined by the concentration of reactant and a proportionality constant called the rate constant. Reactions that are directly proportional to the reactant concentration are called first-
order reactions. First- order rate constants have the units of s−1. In many reactions in biochemistry, there are two reactants. Such reactions are called bimolecular reactions. The rate constants for biomolecular reactions, called second- order rate constants, have the units M−1s−1. 7.2 The Michaelis–
Menten Model Describes the Kinetics of Many Enzymes The kinetic properties of many enzymes are described by the Michaelis–
Menten model. In this model, an enzyme (E) combines with a substrate (S) to form an enzyme– substrate (ES) complex, which can proceed to form a product (P) or to dissociate into E and S. The velocity V0 of formation of product is given by the Michaelis– Menten equation: Page 125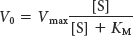
in which Vmax is the reaction velocity when the enzyme is fully saturated with substrate and KM, the Michaelis constant, is the substrate concentration at which the reaction velocity is half maximal. The maximal velocity Vmax is equal to the product of k2, or kcat, and the total concentration of enzyme. The kinetic constant kcat, called the turnover number, is the number of substrate molecules converted into product per unit time at a single catalytic site when the enzyme is fully saturated with substrate. Turnover numbers for most enzymes are between 1 and 104 per second. The ratio of kcat/KM provides information about enzyme efficiency.
7.3 Allosteric Enzymes Are Catalysts and Information Sensors
Allosteric enzymes constitute an important class of enzymes whose catalytic activity can be regulated. These enzymes, which do not conform to Michaelis–
Menten kinetics, have multiple active sites. These active sites display cooperativity, as evidenced by a sigmoidal dependence of reaction velocity on substrate concentration. Regulators of allosteric enzymes can stimulate enzyme activity or inhibit enzyme activity. 7.4 Enzymes Can Be Studied One Molecule at a Time
Many enzymes are now being studied in singulo, at the level of a single molecule. Such studies are important because they yield information that is difficult to obtain in studies of populations of molecules. Single-
molecule methods reveal a distribution of enzyme characteristics rather than an average value as is acquired with the use of ensemble methods.