PROBLEMS
Question 9.1
1. Two by two. Match each term with its description.
Hemoglobin Myoglobin Heme Protoporphyrin Proximal histidine 2,3- Sickle- Bohr effect Carbonic anhydrase Carbamate | Facilitates the formation of protons and bicarbonate The regulation of oxygen binding by hydrogen ions and carbon dioxide Results from the change of a single amino acid in the β chain of hemoglobin Displays tertiary structure only Binds the fifth coordination site in the heme Displays quaternary structure Oxygen- Composed of four pyrrole rings Binds in the center of the hemoglobin tetramer Amino termini structures that stabilize the T state |
Question 9.2
2. Hemoglobin content. The average volume of a red blood cell is 87 mm3. The mean concentration of hemoglobin in red cells is 0.34 g ml−1.
(a) What is the weight of the hemoglobin contained in a red cell?
(b) How many hemoglobin molecules are there in a red cell?
(c) Could the hemoglobin concentration in red cells be much higher than the observed value? (Hint: Suppose that a red cell contained a crystalline array of hemoglobin molecules in a cubic lattice with 65-
Question 9.3
3. Iron content. How much iron is there in the hemoglobin of a 70-
Question 9.4
4. Oxygenating myoglobin. The myoglobin content of some human muscles is about 8 g kg−1. In sperm whale, the myoglobin content of muscle is about 80 g kg−1.
(a) How much O2 is bound to myoglobin in human muscle and in sperm-
(b) The amount of oxygen dissolved in tissue water (in equilibrium with venous blood) at 37°C is about 3.5 × 10−5 M. What is the ratio of oxygen bound to myoglobin to that directly dissolved in the water of sperm-
Question 9.5
5. Cooperation is good. What is the physiological significance of the cooperative binding of oxygen by hemoglobin? ✓ 7
Question 9.6
6. Suddenly breaking into pieces. When crystals of deoxyhemoglobin are exposed to oxygen, the crystals shatter. Why? ✓ 7
Question 9.7
7. Hybrid vigor. The oxygen-
Question 9.8
8. Mom to baby. What accounts for the fact that fetal hemoglobin has a higher oxygen affinity than maternal hemoglobin? ✓ 7
Question 9.9
9. Structural damage. How does hemoglobin S cause tissue damage?
Question 9.10
10. Saving grace. Hemoglobin A inhibits the formation of the long fibers of hemoglobin S and the subsequent sickling of the red cell on deoxygenation. Why does hemoglobin A have this effect?
Question 9.11
11. Screening the biosphere. The first protein to have its structure determined was myoglobin from sperm whales. Propose an explanation for the observation that sperm-
Question 9.12
12. Fits in the pocket. Describe the role of 2,3-
Question 9.13
13. High-
Question 9.14
14. Blood doping. Endurance athletes sometimes try an illegal method of blood doping called autologous transfusion. Some blood from the athlete is removed well before competition, and then transfused back into the athlete just before competition.
(a) Why might blood transfusion benefit the athlete?
(b) With time, stored red blood cells become depleted in 2,3-
Question 9.15
15. A bad lecture? What is the Bohr effect, and what is its chemical basis? ✓ 8
Question 9.16
16. I’ll have the lobster. Arthropods such as lobsters have oxygen carriers quite different from hemoglobin. The oxygen-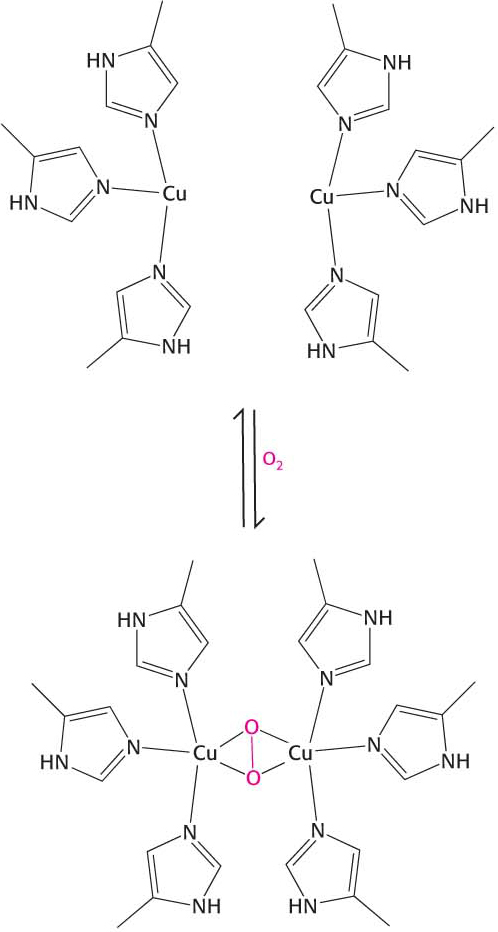
Question 9.17
17. Successful substitution. Blood cells from some birds do not contain 2,3-
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 
Data Interpretation Problem
Question 9.18
18. Leaning to the left or to the right. The adjoining illustration shows several oxygen-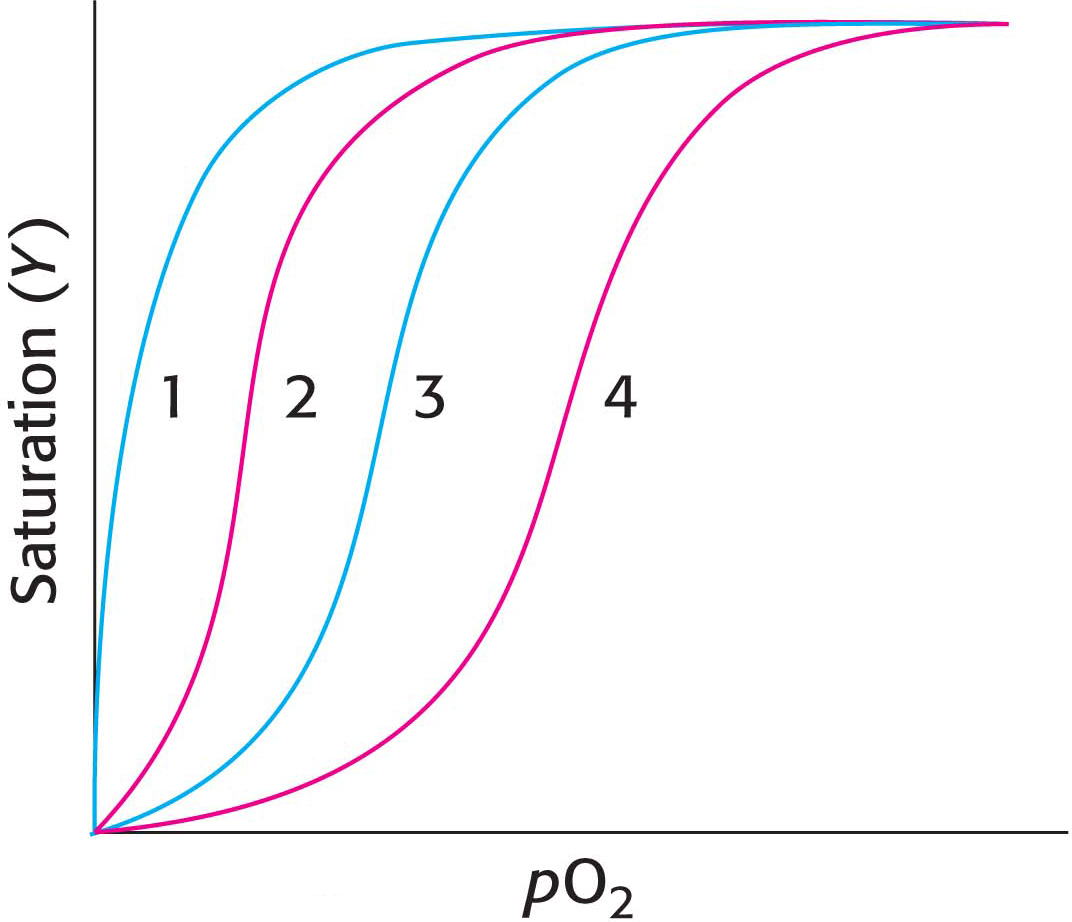
(a) Decrease in CO2
(b) Increase in 2,3-
(c) Increase in pH
(d) Loss of quaternary structure
Chapter Integration Problem
Question 9.19
19. Location is everything. As shown in Figure 9.10, 2,3-
Challenge Problems
Question 9.20
20. Release kinetics. The dissociation constant KD for the release of oxygen from oxymyoglobin is 10−6 M, where KD is defined as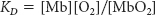
The rate constant for the combination of O2 with myoglobin is 2 × 107 M−1 s−1.
(a) What is the rate constant for the dissociation of O2 from oxymyoglobin?
(b) What is the mean duration of the oxymyoglobin complex?
Question 9.21
21. Tuning proton affinity. The pKa of an acid depends partly on its environment. Predict the effect of each of the following environmental changes on the pKa of a glutamic acid side chain. ✓ 8
(a) A lysine side chain is brought into proximity.
(b) The terminal carboxyl group of the protein is brought into close proximity.
(c) The glutamic acid side chain is shifted from the outside of the protein to a nonpolar site inside.
Question 9.22
22. Deadly gas. Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas that binds to hemoglobin at an oxygen-
Question 9.23
23. Carrying a load. Suppose that you are climbing a high mountain and the oxygen partial pressure in the air is reduced to 75 torr. Estimate the percentage of the oxygen-
Question 9.24
24. A disconnect. With the use of recombinant DNA techniques (Chapter 41), hemoglobin has been prepared in which the proximal histidine residues in both the a and the β subunits have been replaced by glycine. The imidazole ring from the histidine residue can be replaced by adding free imidazole in solution.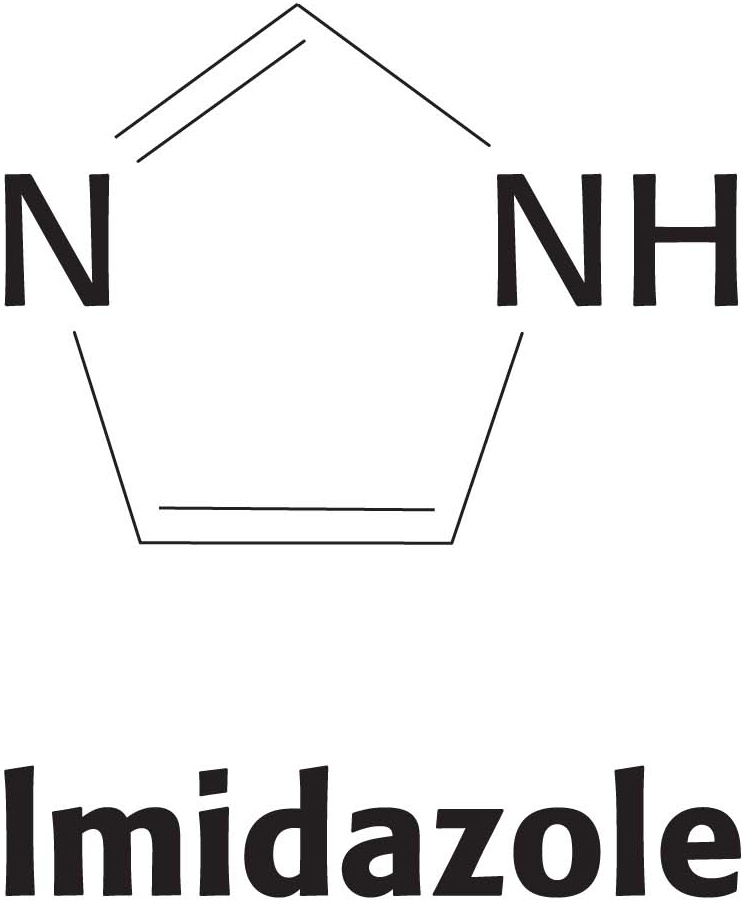
Would you expect this modified hemoglobin to show cooperativity in oxygen binding? Why or why not?
Question 9.25
25. Parasitic effect. When Plasmodium falciparum, a protozoan, lives inside red blood cells, the metabolism of the parasite tends to release acid. What effect is the presence of acid likely to have on the oxygen-
Selected Readings for this chapter can be found online at www.whfreeman.com/