Chapter 2. EXPERIMENT TWO: Oxidation of Isoborneol with Bleach
Introduction
Before lab, read about sublimation, drying agents, and liquid-liquid extraction in Ch 3 of Making the Connections. As needed, review alcohol oxidation in your Organic Chemistry text.
Safety:
acetic acid: corrosive, highly irritating vapors
isoborneol: irritant
camphor: flammable, irritant
hexanes:flammable, toxic
sodium hypochlorite: corrosive, toxic
sodium bisulfite: causes serious eye damage, harmful if swallowed, harmful to aquatic life
magnesium sulfate:

Work with a lab partner for this experiment. In this experiment, bleach (sodium hypochlorite, NaOCl) will oxidize isoborneol to camphor, which will be purified by sublimation. Camphor is a natural product, isolated from the wood of the camphor tree, native to China.
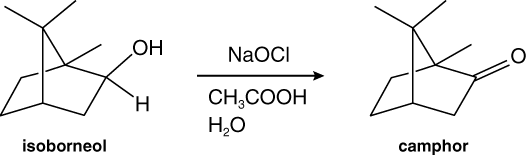
This experiment is classified as Green Chemistry. Green chemical procedures employ environmentally safe reagents, creating waste streams that are less toxic. Further, Green reactions are efficient, thereby minimizing energy use. The oxidation of alcohols is traditionally affected with chromium-based oxidizing agents, which are extremely toxic and carcinogenic. Chromium compounds can leach into waterways, adversely affecting health of downstream populations. A high profile case of chromium poisoning in a southern California community was dramatized in the movie Erin Brockovitch. Unlike chromium, household bleach poses minimal risk to people and the environment. The choice of a benign oxidant qualifies this experiment as Green Chemistry.
You will purify camphor by sublimation: direct conversion of a solid to a gas. Solids that readily vaporize at relatively low temperatures are good candidates for sublimation (e.g. dry ice). Iodine, for example, can be vaporized at low heat, leaving nonvolatile impurities in the solid state. The resulting pure gaseous iodine can be cooled and isolated as a solid.

Experimental Procedure
Run the experiment with a lab partner. In a 50-mL Erlenmeyer flask equipped with a magnetic stirring bar, vigorously stir isoborneol (1.3 g) with glacial acetic acid (roughly 1 mL). Add the NaOCl solution (1.7 mL) and heat to 50°C. Measure another portion of NaOCl (15 mL) into a separatory funnel secured over the flask. Use the separatory funnel to deliver the NaOCl dropwise over a period of 10 minutes. Use a thermometer to monitor the temperature of the reaction, keeping it at 50°C (Set your hotplate to roughly 75 °C to achieve this.) If your reaction overheats, use an ice bath to cool it. When addition is complete, seal the flask with Paraflim and stir.
Roughly every 5 minutes, check that the reaction contains excess NaOCl by dipping a glass rod into the solution and touching it to a strip of starch-iodide paper. A positive test is indicated by a purple color. If the test is negative, add enough NaOCl (in ~1 mL portions) to give a positive test. When the reaction is complete (15-20 minutes), test again for excess NaOCl. Then add enough saturated sodium bisulfite (NaHSO3) dropwise to give a negative test (colorless).
Cool the reaction mixture in an ice-water bath and collect the product by vacuum filtration. Pass air through the solid for a few minutes to dry it, and then place it in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask. Add hexanes until the camphor is fully dissolved. If your product contains a significant quantity of adsorbed water, you will notice two liquid layers form when hexanes is added or a significant quantity of water droplets in the hexanes. If this occurs, use a separatory funnel to separate the hexanes and water layers. (Your TA will demonstrate how to do this in the lab.)
Dry the resulting hexanes solution by adding enough MgSO4 to the solution (usually a few small spatula scoops) that it moves freely (does not stick) in the flask when swirled. Gravity filter the dry (meaning anhydrous) hexanes solution through your stemless funnel into a clean Erlenmeyer flask, and rinse a few times with hexanes. Add a boiling chip or stir bar and evaporate the hexanes by warming on a hotplate set to about 80 °C.
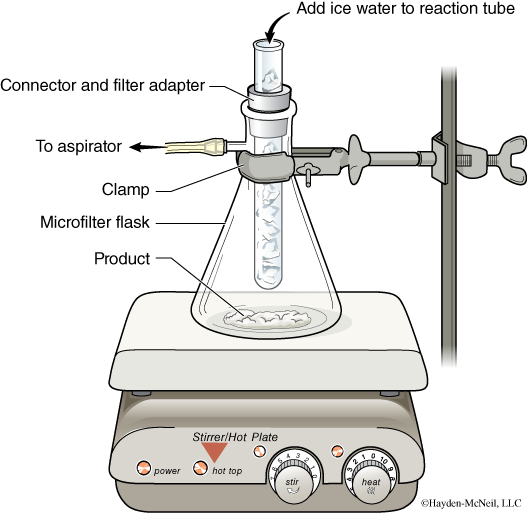
Set up a sublimation apparatus (illustrated below), load the dried product in it, and sublime the product using an aspirator vacuum. If your product is not subliming after 5 minutes or so, begin to heat your hotplate very gently.
Tips for a successful sublimation:
- Use gentle heat.
- Constantly change the ice water in the “cold finger” to make sure it is as cold as possible.
- Make sure you are using an aspirator that pulls an adequate vacuum.
- The inside of your sidearm flask must be dry. Also make sure water does not collect around the connector and filter adapter.
- When you are ready to collect the sublimed product from the cold finger, turn off the vacuum first.
Prepare two capillary tubes with a sample of the crude and pure products. Seal the open end of the capillaries using the Bunsen burner. Record melting points of the crude and pure products (this can be done now or during the next lab period).
WASTE DISPOSAL: Dilute all liquid waste in at least 250 mL water. Slowly pour this dilute solution down the sink with vigorously flowing tap water. Remember that bleach is a strong oxidizer, so be especially careful not to mix aqueous and organic waste in this lab.
Write-up Questions
List at least two uses of camphor. Remember to cite your source(s).
Proton and carbon-13 NMR can provide evidence that you have successfully oxidized isoborneol to camphor. List key peaks you would look for in the 1H and 13C NMR spectra (at least one from 1H and one from 13C) of the product to determine if the oxidation was a success.
In addition to NMR spectroscopy, describe one other type of spectroscopy that might be particularly useful for determining the success or failure of your reaction. Explain your choice.
Using the Twelve Principles of Green Chemistry, explain which principles (by number) make this reaction green. http://www.acs.org/content/acs/en/greenchemistry/what-is-green-chemistry/principles/12-principles-of-green-chemistry.html