COSMIC CONNECTIONS
The Outer Planets: A Comparison
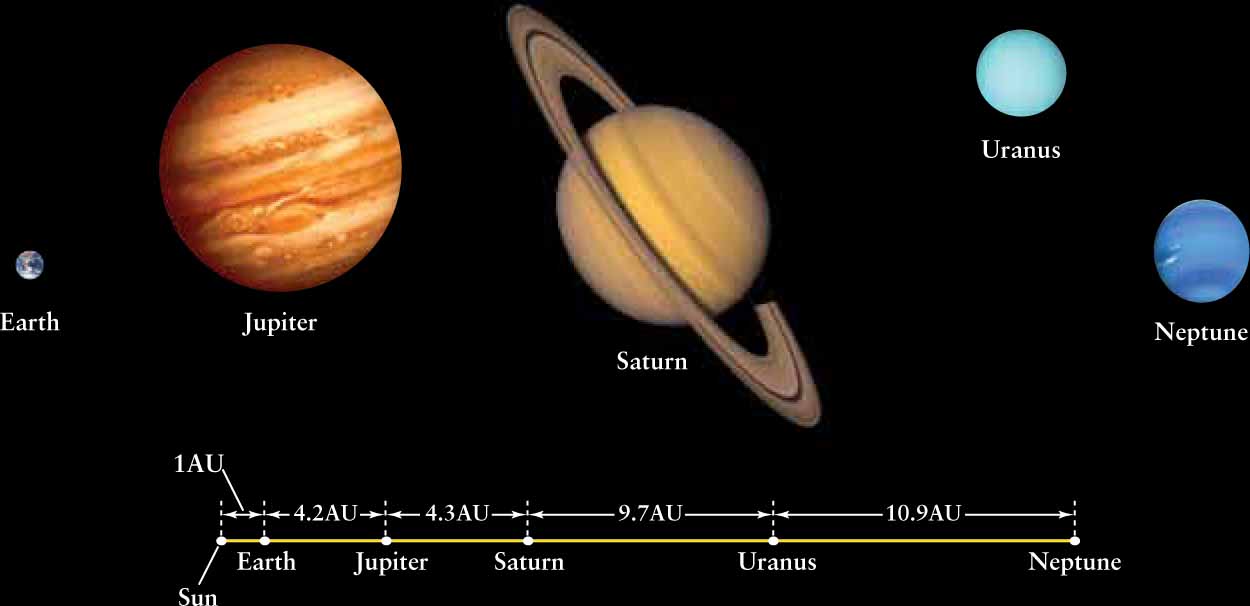
Uranus and Neptune are not simply smaller versions of Jupiter and Saturn. This table summarizes the key differences among the four Jovian planets.
| Interior | Surface | Rings | Atmosphere | Magnetic Field | |
| Jupiter | Terrestrial core, thick liquid metallic hydrogen layer, molecular hydrogen | No solid surface, atmosphere gradually thickens to liquid state, belt and zone structure, hurricanelike features | Yes | Primarily H, He | 19,000 × Earth’s total field; at its cloud layer, 14 × stronger than Earth’s surface field |
| Saturn | Similar to Jupiter, with bigger terrestrial core and less metallic hydrogen | No solid surface, less distinct belt and zone structure than Jupiter | Yes | Primarily H, He | 570 × Earth’s total field; at its cloud layer, ⅔ × Earth’s surface field |
| Uranus | Terrestrial core, liquid water shell, liquid hydrogen and helium mantle | No solid surface, weak belt and zone system, hurricanelike features, color from methane absorption of red, orange, yellow | Yes | Primarily H, He, some CH4 | 50 × Earth’s total field, at its cloud layer, 0.7 × Earth’s surface field |
| Neptune | Similar to Uranus | Similar to Uranus | Yes | Primarily H, He, some CH4 | 35 × Earth’s total field, at its cloud layer, 0.4 × Earth’s surface field |
For detailed comparisons between planets, see Appendices 1 and 2.
*To see the orientations of these magnetic fields relative to the rotation axes of the planets, see Figure 14-8.