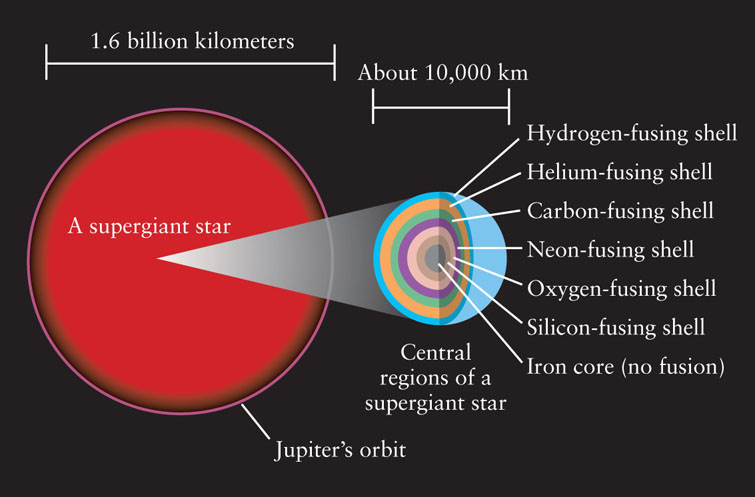
Figure 20-13: The Structure of an Old High-Mass Star Near the end of its life, a star with an initial mass greater than about 8 M⊙ becomes a red supergiant. The star’s overall size can be as large as Jupiter’s orbit around the Sun. The stars energy comes from a series of concentric fusing shells, all combined within a volume roughly the same size as Earth. Nuclear reactions do not occur within the iron core, because fusion reactions that involve iron require an input of energy rather than release it.