- Step 1
- Step 2
- Step 3
- Step 4
- Step 5
- Step 6
- Step 7
- Step 8
- Step 9
- Step 10
- Step 11
- Step 12
- Step 13
Chapter 9. Chapter 9: DNA Makes RNA Makes Protein
Introduction
The table below provides information about a stretch of DNA and its transcription and translation products. Use your knowledge of transcription and translation to complete the following table, filling in the missing DNA and RNA nucleotides and the correct amino acids that would be incorporated into the protein sequence. Assume that the sequences are read from left to right, and that the columns represent transcriptional and translational alignments. After the table has been filled in, label the 5' and 3' ends of the DNA and mRNA and the amino and carboxyl ends of the protein.
| C | DNA double helix | |||||||||||
| T | G | A | ||||||||||
| C | A | U | mRNA transcribed | |||||||||
| G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon | |||||||||
| Trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||
Unpack the Problem: Break this problem into several parts and arrive at a solution using this guided, step-by-step approach.
Solving this problem requires you to apply your understanding of complementary base pairing and the rules that govern the translation of codons into amino acids. The process is iterative. That is, you could start in a number of places and once more cells are filled in, this provides new information for completing more of the table, and so on.
- Part A (steps 1 and 2): Using your knowledge of DNA base pairing and of transcription, you will fill in some of the missing DNA nucleotides.
- Part B (steps 3 and 4): Using your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in most of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part C (step 5): Again, your knowledge of transcription will allow you to complete more of the DNA sequence.
- Part D (steps 6 and 7): Using the genetic code as well as your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in the remainder of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part E (step 8): Now the remaining DNA sequence can be filled in.
- Part F (steps 9 and 10): With all of the nucleotide sequences complete, they can be used to read the genetic code and determine the correct amino acids that would be incorporated if a ribosome was reading this sequence.
- Part G (steps 11-13): Finally, using your knowledge of how polypeptides and polynucleotides form, the direction of each sequence can be determined.
Based on the DNA nucleotides that were provided in the table, drag and drop the four DNA nucleotides (A, C, G, and T) into their correct locations within the DNA double helix portion of the table.
| A. |
| B. |
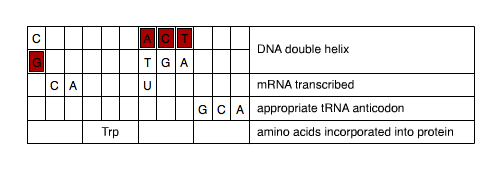

| C | DNA double helix | |||||||||||
| T | G | A | ||||||||||
| C | A | U | mRNA transcribed | |||||||||
| G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon | |||||||||
| Trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||
What is the complementary base of C?
What is the complementary base of T?
Introduction
The table below provides information about a stretch of DNA and its transcription and translation products. Use your knowledge of transcription and translation to complete the following table, filling in the missing DNA and RNA nucleotides and the correct amino acids that would be incorporated into the protein sequence. Assume that the sequences are read from left to right, and that the columns represent transcriptional and translational alignments. After the table has been filled in, label the 5' and 3' ends of the DNA and mRNA and the amino and carboxyl ends of the protein.
| C | DNA double helix | |||||||||||
| T | G | A | ||||||||||
| C | A | U | mRNA transcribed | |||||||||
| G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon | |||||||||
| Trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||
Unpack the Problem: Break this problem into several parts and arrive at a solution using this guided, step-by-step approach.
Solving this problem requires you to apply your understanding of complementary base pairing and the rules that govern the translation of codons into amino acids. The process is iterative. That is, you could start in a number of places and once more cells are filled in, this provides new information for completing more of the table, and so on.
- Part A (steps 1 and 2): Using your knowledge of DNA base pairing and of transcription, you will fill in some of the missing DNA nucleotides.
- Part B (steps 3 and 4): Using your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in most of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part C (step 5): Again, your knowledge of transcription will allow you to complete more of the DNA sequence.
- Part D (steps 6 and 7): Using the genetic code as well as your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in the remainder of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part E (step 8): Now the remaining DNA sequence can be filled in.
- Part F (steps 9 and 10): With all of the nucleotide sequences complete, they can be used to read the genetic code and determine the correct amino acids that would be incorporated if a ribosome was reading this sequence.
- Part G (steps 11-13): Finally, using your knowledge of how polypeptides and polynucleotides form, the direction of each sequence can be determined.
Next, use the mRNA nucleotides CA to assist you in filling in four more of the DNA nucleotides. Drag and drop the four nucleotides (C, G, A, and T) into their correct locations within the DNA double helix portion of the table.
| A. |
| B. |
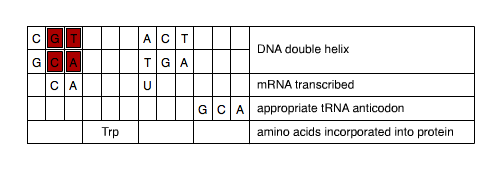

| C | A | C | T | DNA double helix | ||||||||
| G | T | G | A | |||||||||
| C | A | U | mRNA transcribed | |||||||||
| G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon | |||||||||
| Trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||
What is the relationship between the mRNA sequence and each of the DNA strand sequences?
Is it possible to determine from inspection of the table which DNA strand is the template strand?
Introduction
The table below provides information about a stretch of DNA and its transcription and translation products. Use your knowledge of transcription and translation to complete the following table, filling in the missing DNA and RNA nucleotides and the correct amino acids that would be incorporated into the protein sequence. Assume that the sequences are read from left to right, and that the columns represent transcriptional and translational alignments. After the table has been filled in, label the 5' and 3' ends of the DNA and mRNA and the amino and carboxyl ends of the protein.
| C | DNA double helix | |||||||||||
| T | G | A | ||||||||||
| C | A | U | mRNA transcribed | |||||||||
| G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon | |||||||||
| Trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||
Unpack the Problem: Break this problem into several parts and arrive at a solution using this guided, step-by-step approach.
Solving this problem requires you to apply your understanding of complementary base pairing and the rules that govern the translation of codons into amino acids. The process is iterative. That is, you could start in a number of places and once more cells are filled in, this provides new information for completing more of the table, and so on.
- Part A (steps 1 and 2): Using your knowledge of DNA base pairing and of transcription, you will fill in some of the missing DNA nucleotides.
- Part B (steps 3 and 4): Using your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in most of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part C (step 5): Again, your knowledge of transcription will allow you to complete more of the DNA sequence.
- Part D (steps 6 and 7): Using the genetic code as well as your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in the remainder of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part E (step 8): Now the remaining DNA sequence can be filled in.
- Part F (steps 9 and 10): With all of the nucleotide sequences complete, they can be used to read the genetic code and determine the correct amino acids that would be incorporated if a ribosome was reading this sequence.
- Part G (steps 11-13): Finally, using your knowledge of how polypeptides and polynucleotides form, the direction of each sequence can be determined.
If an mRNA codon is ACA, then what is the corresponding tRNA anticodon?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
What is the role of a tRNA anticodon?
What is the relationship between an mRNA codon sequence and its corresponding tRNA anticodon sequence?
Introduction
The table below provides information about a stretch of DNA and its transcription and translation products. Use your knowledge of transcription and translation to complete the following table, filling in the missing DNA and RNA nucleotides and the correct amino acids that would be incorporated into the protein sequence. Assume that the sequences are read from left to right, and that the columns represent transcriptional and translational alignments. After the table has been filled in, label the 5' and 3' ends of the DNA and mRNA and the amino and carboxyl ends of the protein.
| C | DNA double helix | |||||||||||
| T | G | A | ||||||||||
| C | A | U | mRNA transcribed | |||||||||
| G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon | |||||||||
| Trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||
Unpack the Problem: Break this problem into several parts and arrive at a solution using this guided, step-by-step approach.
Solving this problem requires you to apply your understanding of complementary base pairing and the rules that govern the translation of codons into amino acids. The process is iterative. That is, you could start in a number of places and once more cells are filled in, this provides new information for completing more of the table, and so on.
- Part A (steps 1 and 2): Using your knowledge of DNA base pairing and of transcription, you will fill in some of the missing DNA nucleotides.
- Part B (steps 3 and 4): Using your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in most of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part C (step 5): Again, your knowledge of transcription will allow you to complete more of the DNA sequence.
- Part D (steps 6 and 7): Using the genetic code as well as your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in the remainder of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part E (step 8): Now the remaining DNA sequence can be filled in.
- Part F (steps 9 and 10): With all of the nucleotide sequences complete, they can be used to read the genetic code and determine the correct amino acids that would be incorporated if a ribosome was reading this sequence.
- Part G (steps 11-13): Finally, using your knowledge of how polypeptides and polynucleotides form, the direction of each sequence can be determined.
Use your knowledge of codon-anticodon binding to fill in as much of the mRNA and tRNA nucleotides as you can. Drag and drop the nucleotides into the correct location on the table.
| A. |
| B. |
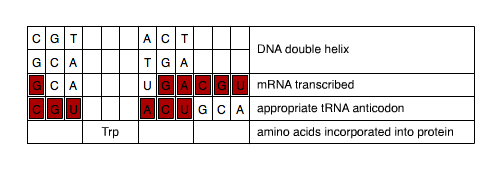

| C | G | T | A | C | T | DNA double helix | ||||||
| G | C | A | T | G | A | |||||||
| C | A | U | mRNA transcribed | |||||||||
| G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon | |||||||||
| Trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||
What is the relationship between an mRNA codon sequence and its corresponding tRNA anticodon sequence?
What is the correspondence between a tRNA anticodon and the 3-nucleotide DNA sequence that codes for the tRNA's cognate codon?
Introduction
The table below provides information about a stretch of DNA and its transcription and translation products. Use your knowledge of transcription and translation to complete the following table, filling in the missing DNA and RNA nucleotides and the correct amino acids that would be incorporated into the protein sequence. Assume that the sequences are read from left to right, and that the columns represent transcriptional and translational alignments. After the table has been filled in, label the 5' and 3' ends of the DNA and mRNA and the amino and carboxyl ends of the protein.
| C | DNA double helix | |||||||||||
| T | G | A | ||||||||||
| C | A | U | mRNA transcribed | |||||||||
| G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon | |||||||||
| Trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||
Unpack the Problem: Break this problem into several parts and arrive at a solution using this guided, step-by-step approach.
Solving this problem requires you to apply your understanding of complementary base pairing and the rules that govern the translation of codons into amino acids. The process is iterative. That is, you could start in a number of places and once more cells are filled in, this provides new information for completing more of the table, and so on.
- Part A (steps 1 and 2): Using your knowledge of DNA base pairing and of transcription, you will fill in some of the missing DNA nucleotides.
- Part B (steps 3 and 4): Using your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in most of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part C (step 5): Again, your knowledge of transcription will allow you to complete more of the DNA sequence.
- Part D (steps 6 and 7): Using the genetic code as well as your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in the remainder of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part E (step 8): Now the remaining DNA sequence can be filled in.
- Part F (steps 9 and 10): With all of the nucleotide sequences complete, they can be used to read the genetic code and determine the correct amino acids that would be incorporated if a ribosome was reading this sequence.
- Part G (steps 11-13): Finally, using your knowledge of how polypeptides and polynucleotides form, the direction of each sequence can be determined.
Fill in the nucleotides in both strands of the rightmost portion of the DNA.
| C | G | T | A | C | T | DNA double helix | ||||||
| G | C | A | T | G | A | |||||||
| G | C | A | U | G | A | C | G | U | mRNA transcribed | |||
| C | G | U | A | C | U | G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon | |||
| Trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||


This step uses the same logic to fill in the DNA sequence as was used in Step 2.]
What is the relationship between the mRNA sequence and each of the DNA strand sequences?
What is the correspondence between a tRNA anticodon and the 3-nucleotide DNA sequence that codes for the tRNA's cognate codon?
Introduction
The table below provides information about a stretch of DNA and its transcription and translation products. Use your knowledge of transcription and translation to complete the following table, filling in the missing DNA and RNA nucleotides and the correct amino acids that would be incorporated into the protein sequence. Assume that the sequences are read from left to right, and that the columns represent transcriptional and translational alignments. After the table has been filled in, label the 5' and 3' ends of the DNA and mRNA and the amino and carboxyl ends of the protein.
| C | DNA double helix | |||||||||||
| T | G | A | ||||||||||
| C | A | U | mRNA transcribed | |||||||||
| G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon | |||||||||
| Trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||
Unpack the Problem: Break this problem into several parts and arrive at a solution using this guided, step-by-step approach.
Solving this problem requires you to apply your understanding of complementary base pairing and the rules that govern the translation of codons into amino acids. The process is iterative. That is, you could start in a number of places and once more cells are filled in, this provides new information for completing more of the table, and so on.
- Part A (steps 1 and 2): Using your knowledge of DNA base pairing and of transcription, you will fill in some of the missing DNA nucleotides.
- Part B (steps 3 and 4): Using your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in most of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part C (step 5): Again, your knowledge of transcription will allow you to complete more of the DNA sequence.
- Part D (steps 6 and 7): Using the genetic code as well as your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in the remainder of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part E (step 8): Now the remaining DNA sequence can be filled in.
- Part F (steps 9 and 10): With all of the nucleotide sequences complete, they can be used to read the genetic code and determine the correct amino acids that would be incorporated if a ribosome was reading this sequence.
- Part G (steps 11-13): Finally, using your knowledge of how polypeptides and polynucleotides form, the direction of each sequence can be determined.
What information does the genetic code table provide?
c Each 3-letter codon corresponds to a tRNA anticodon. [[Incorrect. Codons refer to triplets of mRNA nucleotides that are positioned within the ribosome where they are read in such a way that the corresponding amino acid is incorporated into the growing polypeptide chain. Each codon has only one amino acid (or stop signal) that corresponds to that triplet.]]
| A. |
| B. |
| D. |
| E. |
| F. |
| G. |
The genetic code reveals the correspondence between a codon and an amino acid. True or False?
A ribosome reads each codon from DNA and uses that information to transfer an amino acid from tRNA to a growing polypeptide chain. True or False?
Codons are triplets of mRNA sequence. True or False?
An amino acid is bound to the anticodon of a tRNA. True or False?
tRNA molecules are adapters that bring a codon and its corresponding amino acid into proximity. True or False?
Introduction
The table below provides information about a stretch of DNA and its transcription and translation products. Use your knowledge of transcription and translation to complete the following table, filling in the missing DNA and RNA nucleotides and the correct amino acids that would be incorporated into the protein sequence. Assume that the sequences are read from left to right, and that the columns represent transcriptional and translational alignments. After the table has been filled in, label the 5' and 3' ends of the DNA and mRNA and the amino and carboxyl ends of the protein.
| C | DNA double helix | |||||||||||
| T | G | A | ||||||||||
| C | A | U | mRNA transcribed | |||||||||
| G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon | |||||||||
| Trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||
Unpack the Problem: Break this problem into several parts and arrive at a solution using this guided, step-by-step approach.
Solving this problem requires you to apply your understanding of complementary base pairing and the rules that govern the translation of codons into amino acids. The process is iterative. That is, you could start in a number of places and once more cells are filled in, this provides new information for completing more of the table, and so on.
- Part A (steps 1 and 2): Using your knowledge of DNA base pairing and of transcription, you will fill in some of the missing DNA nucleotides.
- Part B (steps 3 and 4): Using your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in most of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part C (step 5): Again, your knowledge of transcription will allow you to complete more of the DNA sequence.
- Part D (steps 6 and 7): Using the genetic code as well as your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in the remainder of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part E (step 8): Now the remaining DNA sequence can be filled in.
- Part F (steps 9 and 10): With all of the nucleotide sequences complete, they can be used to read the genetic code and determine the correct amino acids that would be incorporated if a ribosome was reading this sequence.
- Part G (steps 11-13): Finally, using your knowledge of how polypeptides and polynucleotides form, the direction of each sequence can be determined.
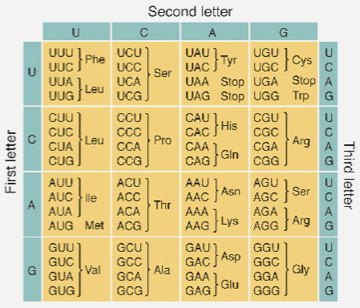
Using the codon table provided, drag and drop the missing tRNA and mRNA nucleotides into the correct location on the table.
| A. |
| B. |
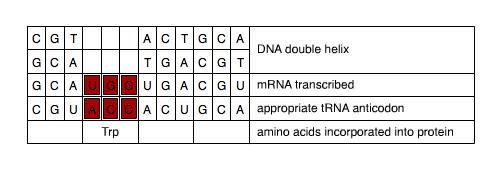

| C | G | T | A | C | T | G | C | A | DNA double helix | |||
| G | C | A | T | G | A | C | G | T | ||||
| G | C | A | U | G | A | C | G | U | mRNA transcribed | |||
| C | G | U | A | C | U | G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon | |||
| Trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||
How many codons correspond to the amino acid tryptophan?
In what class of molecule are the codons in the genetic code table found?
Introduction
The table below provides information about a stretch of DNA and its transcription and translation products. Use your knowledge of transcription and translation to complete the following table, filling in the missing DNA and RNA nucleotides and the correct amino acids that would be incorporated into the protein sequence. Assume that the sequences are read from left to right, and that the columns represent transcriptional and translational alignments. After the table has been filled in, label the 5' and 3' ends of the DNA and mRNA and the amino and carboxyl ends of the protein.
| C | DNA double helix | |||||||||||
| T | G | A | ||||||||||
| C | A | U | mRNA transcribed | |||||||||
| G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon | |||||||||
| Trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||
Unpack the Problem: Break this problem into several parts and arrive at a solution using this guided, step-by-step approach.
Solving this problem requires you to apply your understanding of complementary base pairing and the rules that govern the translation of codons into amino acids. The process is iterative. That is, you could start in a number of places and once more cells are filled in, this provides new information for completing more of the table, and so on.
- Part A (steps 1 and 2): Using your knowledge of DNA base pairing and of transcription, you will fill in some of the missing DNA nucleotides.
- Part B (steps 3 and 4): Using your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in most of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part C (step 5): Again, your knowledge of transcription will allow you to complete more of the DNA sequence.
- Part D (steps 6 and 7): Using the genetic code as well as your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in the remainder of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part E (step 8): Now the remaining DNA sequence can be filled in.
- Part F (steps 9 and 10): With all of the nucleotide sequences complete, they can be used to read the genetic code and determine the correct amino acids that would be incorporated if a ribosome was reading this sequence.
- Part G (steps 11-13): Finally, using your knowledge of how polypeptides and polynucleotides form, the direction of each sequence can be determined.
Fill in the nucleotides in both strands of the rightmost portion of the DNA.
| C | G | T | A | C | T | G | C | A | DNA double helix | |||
| G | C | A | T | G | A | C | G | T | ||||
| G | C | A | U | G | G | U | G | A | C | G | U | mRNA transcribed |
| C | G | U | A | C | C | A | C | U | G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon |
| Trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||


This step uses the same logic to fill in the DNA sequence as was used in Steps 2 and 5.
What is the relationship between the mRNA sequence and each of the DNA strand sequences?
What is the correspondence between a tRNA anticodon and the 3-nucleotide DNA sequence that codes for the tRNA's cognate codon?
Introduction
The table below provides information about a stretch of DNA and its transcription and translation products. Use your knowledge of transcription and translation to complete the following table, filling in the missing DNA and RNA nucleotides and the correct amino acids that would be incorporated into the protein sequence. Assume that the sequences are read from left to right, and that the columns represent transcriptional and translational alignments. After the table has been filled in, label the 5' and 3' ends of the DNA and mRNA and the amino and carboxyl ends of the protein.
| C | DNA double helix | |||||||||||
| T | G | A | ||||||||||
| C | A | U | mRNA transcribed | |||||||||
| G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon | |||||||||
| Trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||
Unpack the Problem: Break this problem into several parts and arrive at a solution using this guided, step-by-step approach.
Solving this problem requires you to apply your understanding of complementary base pairing and the rules that govern the translation of codons into amino acids. The process is iterative. That is, you could start in a number of places and once more cells are filled in, this provides new information for completing more of the table, and so on.
- Part A (steps 1 and 2): Using your knowledge of DNA base pairing and of transcription, you will fill in some of the missing DNA nucleotides.
- Part B (steps 3 and 4): Using your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in most of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part C (step 5): Again, your knowledge of transcription will allow you to complete more of the DNA sequence.
- Part D (steps 6 and 7): Using the genetic code as well as your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in the remainder of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part E (step 8): Now the remaining DNA sequence can be filled in.
- Part F (steps 9 and 10): With all of the nucleotide sequences complete, they can be used to read the genetic code and determine the correct amino acids that would be incorporated if a ribosome was reading this sequence.
- Part G (steps 11-13): Finally, using your knowledge of how polypeptides and polynucleotides form, the direction of each sequence can be determined.
MC: Now that the DNA, mRNA, and tRNA sequences are complete, fill in the row titled, "amino acids incorporated into protein." Assume that the sequence is being translated by a ribosome. Use the codon table below to help fill in the table.

| C | G | T | A | C | C | A | C | T | G | C | A | DNA double helix |
| G | C | A | T | G | G | T | G | A | C | G | T | |
| G | C | A | U | G | A | C | G | U | mRNA transcribed | |||
| C | G | U | A | C | U | G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon | |||
| trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||
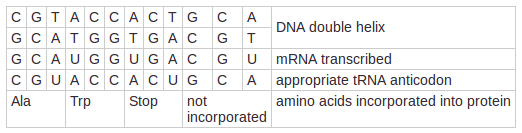

Which sequence is used to find the first amino acid?
In a ribosome, when a tRNA binds to the codon UGA, what happens?
During translation in a ribosome, what happens to the mRNA codons that follow after a stop codon has been read?
Introduction
The table below provides information about a stretch of DNA and its transcription and translation products. Use your knowledge of transcription and translation to complete the following table, filling in the missing DNA and RNA nucleotides and the correct amino acids that would be incorporated into the protein sequence. Assume that the sequences are read from left to right, and that the columns represent transcriptional and translational alignments. After the table has been filled in, label the 5' and 3' ends of the DNA and mRNA and the amino and carboxyl ends of the protein.
| C | DNA double helix | |||||||||||
| T | G | A | ||||||||||
| C | A | U | mRNA transcribed | |||||||||
| G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon | |||||||||
| Trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||
Unpack the Problem: Break this problem into several parts and arrive at a solution using this guided, step-by-step approach.
Solving this problem requires you to apply your understanding of complementary base pairing and the rules that govern the translation of codons into amino acids. The process is iterative. That is, you could start in a number of places and once more cells are filled in, this provides new information for completing more of the table, and so on.
- Part A (steps 1 and 2): Using your knowledge of DNA base pairing and of transcription, you will fill in some of the missing DNA nucleotides.
- Part B (steps 3 and 4): Using your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in most of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part C (step 5): Again, your knowledge of transcription will allow you to complete more of the DNA sequence.
- Part D (steps 6 and 7): Using the genetic code as well as your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in the remainder of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part E (step 8): Now the remaining DNA sequence can be filled in.
- Part F (steps 9 and 10): With all of the nucleotide sequences complete, they can be used to read the genetic code and determine the correct amino acids that would be incorporated if a ribosome was reading this sequence.
- Part G (steps 11-13): Finally, using your knowledge of how polypeptides and polynucleotides form, the direction of each sequence can be determined.
If the sequence in our table was read by a ribosome, which of the following represents the correct amino acid sequence, including the correct placement of the amino terminus and the carboxyl terminus?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
| E. |
| F. |
How are the amino and carboxyl molecules added to the ends of a polypeptide chain?
In a ribosome, when a tRNA binds to the codon UGA, what happens?
During translation in a ribosome, what happens to the mRNA codons that follow after a stop codon has been read?
Introduction
The table below provides information about a stretch of DNA and its transcription and translation products. Use your knowledge of transcription and translation to complete the following table, filling in the missing DNA and RNA nucleotides and the correct amino acids that would be incorporated into the protein sequence. Assume that the sequences are read from left to right, and that the columns represent transcriptional and translational alignments. After the table has been filled in, label the 5' and 3' ends of the DNA and mRNA and the amino and carboxyl ends of the protein.
| C | DNA double helix | |||||||||||
| T | G | A | ||||||||||
| C | A | U | mRNA transcribed | |||||||||
| G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon | |||||||||
| Trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||
Unpack the Problem: Break this problem into several parts and arrive at a solution using this guided, step-by-step approach.
Solving this problem requires you to apply your understanding of complementary base pairing and the rules that govern the translation of codons into amino acids. The process is iterative. That is, you could start in a number of places and once more cells are filled in, this provides new information for completing more of the table, and so on.
- Part A (steps 1 and 2): Using your knowledge of DNA base pairing and of transcription, you will fill in some of the missing DNA nucleotides.
- Part B (steps 3 and 4): Using your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in most of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part C (step 5): Again, your knowledge of transcription will allow you to complete more of the DNA sequence.
- Part D (steps 6 and 7): Using the genetic code as well as your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in the remainder of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part E (step 8): Now the remaining DNA sequence can be filled in.
- Part F (steps 9 and 10): With all of the nucleotide sequences complete, they can be used to read the genetic code and determine the correct amino acids that would be incorporated if a ribosome was reading this sequence.
- Part G (steps 11-13): Finally, using your knowledge of how polypeptides and polynucleotides form, the direction of each sequence can be determined.
Which of the following is the correct notation of the 5' and 3' ends of the DNA sequence?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
In a double helix, are the two strands of DNA oriented in the same or opposite orientation?
Proper orientation of this DNA sequence is in relation to the RNA transcript. With that in mind, are the RNA transcript and the DNA template strand parallel or antiparallel to each other?
Introduction
The table below provides information about a stretch of DNA and its transcription and translation products. Use your knowledge of transcription and translation to complete the following table, filling in the missing DNA and RNA nucleotides and the correct amino acids that would be incorporated into the protein sequence. Assume that the sequences are read from left to right, and that the columns represent transcriptional and translational alignments. After the table has been filled in, label the 5' and 3' ends of the DNA and mRNA and the amino and carboxyl ends of the protein.
| C | DNA double helix | |||||||||||
| T | G | A | ||||||||||
| C | A | U | mRNA transcribed | |||||||||
| G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon | |||||||||
| Trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||
Unpack the Problem: Break this problem into several parts and arrive at a solution using this guided, step-by-step approach.
Solving this problem requires you to apply your understanding of complementary base pairing and the rules that govern the translation of codons into amino acids. The process is iterative. That is, you could start in a number of places and once more cells are filled in, this provides new information for completing more of the table, and so on.
- Part A (steps 1 and 2): Using your knowledge of DNA base pairing and of transcription, you will fill in some of the missing DNA nucleotides.
- Part B (steps 3 and 4): Using your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in most of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part C (step 5): Again, your knowledge of transcription will allow you to complete more of the DNA sequence.
- Part D (steps 6 and 7): Using the genetic code as well as your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in the remainder of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part E (step 8): Now the remaining DNA sequence can be filled in.
- Part F (steps 9 and 10): With all of the nucleotide sequences complete, they can be used to read the genetic code and determine the correct amino acids that would be incorporated if a ribosome was reading this sequence.
- Part G (steps 11-13): Finally, using your knowledge of how polypeptides and polynucleotides form, the direction of each sequence can be determined.
Which of the following is the correct notation of the 5' and 3' ends of the mRNA transcript?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
By convention, RNA transcripts are written in a specific direction, which is
Introduction
The table below provides information about a stretch of DNA and its transcription and translation products. Use your knowledge of transcription and translation to complete the following table, filling in the missing DNA and RNA nucleotides and the correct amino acids that would be incorporated into the protein sequence. Assume that the sequences are read from left to right, and that the columns represent transcriptional and translational alignments. After the table has been filled in, label the 5' and 3' ends of the DNA and mRNA and the amino and carboxyl ends of the protein.
| C | DNA double helix | |||||||||||
| T | G | A | ||||||||||
| C | A | U | mRNA transcribed | |||||||||
| G | C | A | appropriate tRNA anticodon | |||||||||
| Trp | amino acids incorporated into protein | |||||||||||
Unpack the Problem: Break this problem into several parts and arrive at a solution using this guided, step-by-step approach.
Solving this problem requires you to apply your understanding of complementary base pairing and the rules that govern the translation of codons into amino acids. The process is iterative. That is, you could start in a number of places and once more cells are filled in, this provides new information for completing more of the table, and so on.
- Part A (steps 1 and 2): Using your knowledge of DNA base pairing and of transcription, you will fill in some of the missing DNA nucleotides.
- Part B (steps 3 and 4): Using your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in most of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part C (step 5): Again, your knowledge of transcription will allow you to complete more of the DNA sequence.
- Part D (steps 6 and 7): Using the genetic code as well as your knowledge of mRNA/tRNA base pairing, you will fill in the remainder of the missing mRNA and tRNA sequences.
- Part E (step 8): Now the remaining DNA sequence can be filled in.
- Part F (steps 9 and 10): With all of the nucleotide sequences complete, they can be used to read the genetic code and determine the correct amino acids that would be incorporated if a ribosome was reading this sequence.
- Part G (steps 11-13): Finally, using your knowledge of how polypeptides and polynucleotides form, the direction of each sequence can be determined.
Which DNA strand was used as the template for transcription?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
During transcription, in what direction does the RNA grow?
Are the RNA transcript and the DNA template strand parallel or antiparallel to each other?
Conclusion
Within the sequence of DNA resides the information to manufacture specific proteins inside a cell. The cellular machinery uses a DNA sequence as a template, and RNA polymerase reads it and synthesizes an mRNA transcript using the rules of complementary base pairing. The mRNA transcript interacts with ribosomes and the adapter molecules, tRNAs, to build a polypeptide chain that folds into a protein. Again it is complementary base pairing rules that determine which tRNA binds to a codon of the mRNA. The genetic code reveals the relationships between each mRNA codon and its corresponding amino acid. It is the tRNA molecules that functionally perform the code conversion: translating a nucleotide sequence into a sequence of amino acids. In this problem you have used base-pairing rules and the genetic code to reinforce how information encoded in DNA is retained and transferred through RNA molecules to ultimately build a protein.