Women, War, and the Battle for Suffrage
Printed Page 658
Women had made real strides during the Progressive Era, and war presented new opportunities. More than 25,000 women served in France. About half were nurses. The others drove ambulances; ran canteens for the Salvation Army, Red Cross, and YMCA; worked with French civilians in devastated areas; and acted as telephone operators and war correspondents. Like men who joined the war effort, they believed that they were taking part in a great national venture. “I am more than willing to live as a soldier and know of the hardships I would have to undergo,” one canteen worker declared when applying to go overseas, “but I want to help my country. … I want … to do the real work.” And like men, women struggled against disillusionment in France. One woman explained: “Over in America, we thought we knew something about the war … but when you get here the difference is [like the one between] studying the laws of electricity and being struck by lightning.”
At home, long-standing barriers against hiring women fell when millions of workingmen became soldiers and few new immigrant workers crossed the Atlantic. Tens of thousands of women found work in defense plants as welders, metalworkers, and heavy machine operators and with the railroads. A black woman, a domestic before the war, celebrated her job as a laborer in a railroad yard: “We … do not have to work as hard as at housework which requires us to be on duty from six o’clock in the morning until nine or ten at night, with might[y] little time off and at very poor wages.” Other women found white-collar work. Between 1910 and 1920, the number of women clerks doubled. Before the war ended, more than a million women had found work in war industries.
The most dramatic advance for women came in the political arena. Adopting a state-by-state approach before the war, suffragists had achieved some success (Map 22.4). More commonly, voting rights for women met strong hostility and defeat. After 1910, suffrage leaders added a federal campaign to amend the Constitution to the traditional state-by-state strategy for suffrage.
The radical wing of the suffragists, led by Alice Paul, picketed the White House, where the marchers unfurled banners that proclaimed “America Is Not a Democracy. Twenty Million Women Are Denied the Right to Vote.” They chained themselves to fences and went to jail, where many engaged in hunger strikes. But membership in the mainstream organization, the National American Woman Suffrage Association, led by Carrie Chapman Catt, soared to some two million. Seeing the handwriting on the wall, the Republican and Progressive parties endorsed woman suffrage in 1916.
CHAPTER LOCATOR
What was Woodrow Wilson’s foreign policy agenda?
What role did the United States play in World War I?
What impact did the war have on the home front?
What part did Woodrow Wilson play at the Paris peace conference?
Why was America’s transition from war to peace so turbulent?
Conclusion: What was the domestic cost of foreign victory?
 LearningCurve
LearningCurve
Check what you know.
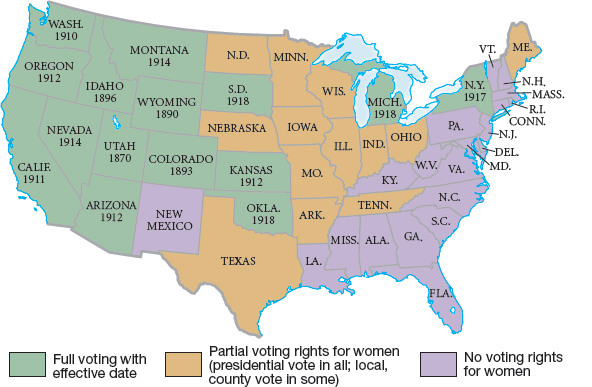
In 1918, Wilson gave his support to suffrage, calling the amendment “vital to the winning of the war.” He conceded that it would be wrong not to reward the wartime “partnership of suffering and sacrifice” with a “partnership of privilege and right.” By linking their cause to the wartime emphasis on national unity, the advocates of woman suffrage finally triumphed. In 1919, Congress passed the Nineteenth Amendment (woman suffrage), granting women the vote, and by August 1920 the required two-thirds of the states had ratified it.
Nineteenth Amendment (woman suffrage)
 Constitutional amendment granting women the vote. Congress passed the amendment in 1919, and it was ratified in August 1920. Like proponents of prohibition, the advocates of woman suffrage triumphed by linking their cause to the war.
Constitutional amendment granting women the vote. Congress passed the amendment in 1919, and it was ratified in August 1920. Like proponents of prohibition, the advocates of woman suffrage triumphed by linking their cause to the war.