A Growing War in Vietnam
Printed Page 874
In 1963, Kennedy criticized the idea of “a Pax Americana enforced on the world by American weapons of war,” but he had already increased the flow of those weapons into South Vietnam. Kennedy’s strong anticommunism and attachment to a vigorous foreign policy prepared him to expand the commitment that he had inherited from Eisenhower.
By the time Kennedy took office, more than $1 billion in aid and seven hundred U.S. military advisers had failed to stabilize South Vietnam. Two major obstacles stood in the way. First, the South Vietnamese insurgents — whom Americans called Vietcong — were an indigenous force whose initiative came from within. Because the Saigon government refused to hold elections, the rebels saw no choice but to take up arms. Increasingly, Ho Chi Minh’s Communist government in North Vietnam supplied them with weapons and soldiers.
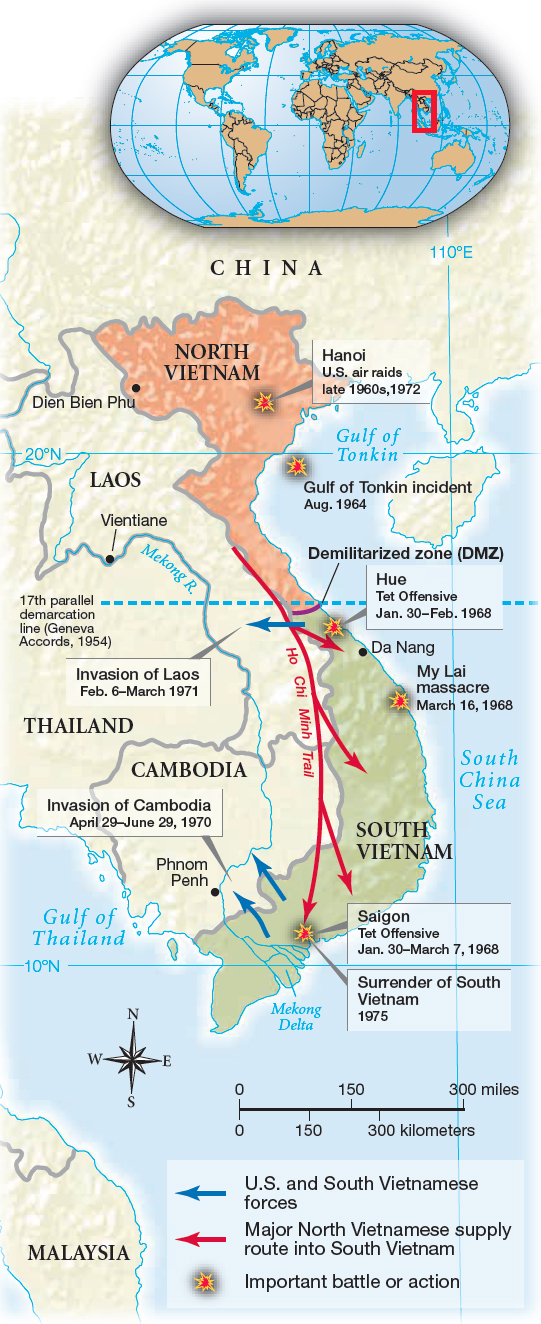
Second, the South Vietnamese government refused to satisfy insurgents’ demands, but the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) could not defeat them militarily. Ngo Dinh Diem, South Vietnam’s premier from 1954 to 1963, chose self-serving military leaders for their personal loyalty rather than for their effectiveness. Many South Vietnamese, the majority of whom were Buddhists, saw the Catholic Diem as a corrupt and brutal tool of the West. The growing intervention by North Vietnam made matters worse. In 1960, the Hanoi government established the National Liberation Front, composed of South Vietnamese rebels but directed by the northern army. In addition, Hanoi constructed a network of infiltration routes, called the Ho Chi Minh Trail, in neighboring Laos and Cambodia, through which it sent people and supplies to help liberate the South (Map 29.2). Violence escalated between 1960 and 1963, bringing the Saigon government close to collapse.
CHAPTER LOCATOR
How did U.S. foreign policy change under Kennedy?
Why did Johnson escalate American involvement in Vietnam?
How did the war in Vietnam polarize the nation?
How did U.S. foreign policy change under Nixon?
Conclusion: Was Vietnam an unwinnable war?
 LearningCurve
LearningCurve
Check what you know.
In response, Kennedy gradually escalated the U.S. commitment. By the spring of 1963, military aid had doubled, and 9,000 Americans served in Vietnam as military advisers, occasionally participating in actual combat. The South Vietnamese government promised reform but never made good on its promises.
American officials assumed that technology and sheer power could win in Vietnam. Yet advanced weapons were ill suited to the guerrilla warfare practiced by the enemy, whose surprise attacks were designed to weaken support for the South Vietnamese government. Moreover, U.S. weapons and strategy harmed the very people they were intended to save. Thousands of peasants were uprooted or fell victim to bombs — containing the highly flammable substance napalm —dropped by the South Vietnamese air force to quell the Vietcong. In 1962, U.S. planes began to spray herbicides such as Agent Orange to destroy the Vietcong’s jungle hideouts and food supply.
 Herbicide used extensively during the Vietnam War to destroy the Vietcong’s jungle hideouts and food supply. Its use was later linked to a wide range of illnesses that veterans and the Vietnamese suffered after the war, including birth defects, cancer, and skin disorders.
Herbicide used extensively during the Vietnam War to destroy the Vietcong’s jungle hideouts and food supply. Its use was later linked to a wide range of illnesses that veterans and the Vietnamese suffered after the war, including birth defects, cancer, and skin disorders.
With tacit permission from Washington, South Vietnamese military leaders executed a coup against Diem and his brother, who headed the secret police, in November 1963. Kennedy expressed shock at the murders but indicated no change in policy. In a speech to be given on the day he was assassinated, Kennedy referred specifically to Southeast Asia and warned, “We dare not weary of the task.” At his death, 16,700 Americans were stationed in Vietnam, and 100 had died there.
QUICK REVIEW
Question
Why did Kennedy believe that engagement in Vietnam was crucial to his foreign policy?