The Atlantic Slave Trade and the Growth of Slavery
Printed Page 123
The number of southerners of African ancestry (nearly all of them slaves) rocketed from just over 20,000 in 1700 to well over 400,000 in 1770. The black population increased nearly three times faster than the South’s briskly growing white population. Consequently, the proportion of southerners of African ancestry grew from 20 percent in 1700 to 40 percent in 1770.
Southern colonists clustered into two distinct geographic and agricultural zones. The colonies in the upper South, surrounding the Chesapeake Bay, specialized in growing tobacco, as they had since the early seventeenth century. Throughout the eighteenth century, nine out of ten southern whites and eight out of ten southern blacks lived in the Chesapeake region. The upper South retained a white majority during the eighteenth century.
CHAPTER LOCATOR
How did the North American colonies change in the eighteenth century?
What changed in New England life and culture?
What spurred the growth of the middle colonies?
Why did slavery become the defining feature of the southern colonies?
What experiences tended to unify colonists in British North America?
Conclusion: What was the dual identity of British North American colonists?
 LearningCurve
LearningCurve
Check what you know.
In the lower South, a much smaller cluster of colonists inhabited the coastal region and specialized in the production of rice and indigo (a plant used to make blue dye). Lower South colonists made up only 5 percent of the total population of the southern colonies in 1700 but inched upward to 15 percent by 1770. South Carolina was the sole British colony along the southern Atlantic coast until 1732. (North Carolina, founded in 1711, was largely an extension of the Chesapeake region.) Georgia was founded in 1732 as a refuge for poor people from England. Georgia’s leaders banned slaves from 1735 to 1750, but few settlers arrived until after 1750, when the prohibition on slavery was lifted and slaves flooded in. In South Carolina, in contrast to Georgia and every other British mainland colony, slaves outnumbered whites almost two to one; in some low-country districts, the ratio of blacks to whites exceeded ten to one.
The enormous growth in the South’s slave population occurred through natural increase and the flourishing Atlantic slave trade (Map 5.3 and Table 5.1). Slave ships brought almost 300,000 Africans to British North America between 1619 and 1780. Of these Africans, 95 percent arrived in the South and 96 percent arrived during the eighteenth century. Unlike indentured servants and redemptioners, these Africans did not choose to come to the colonies. Most of them had been born into free families in villages located within a few hundred miles of the West African coast.
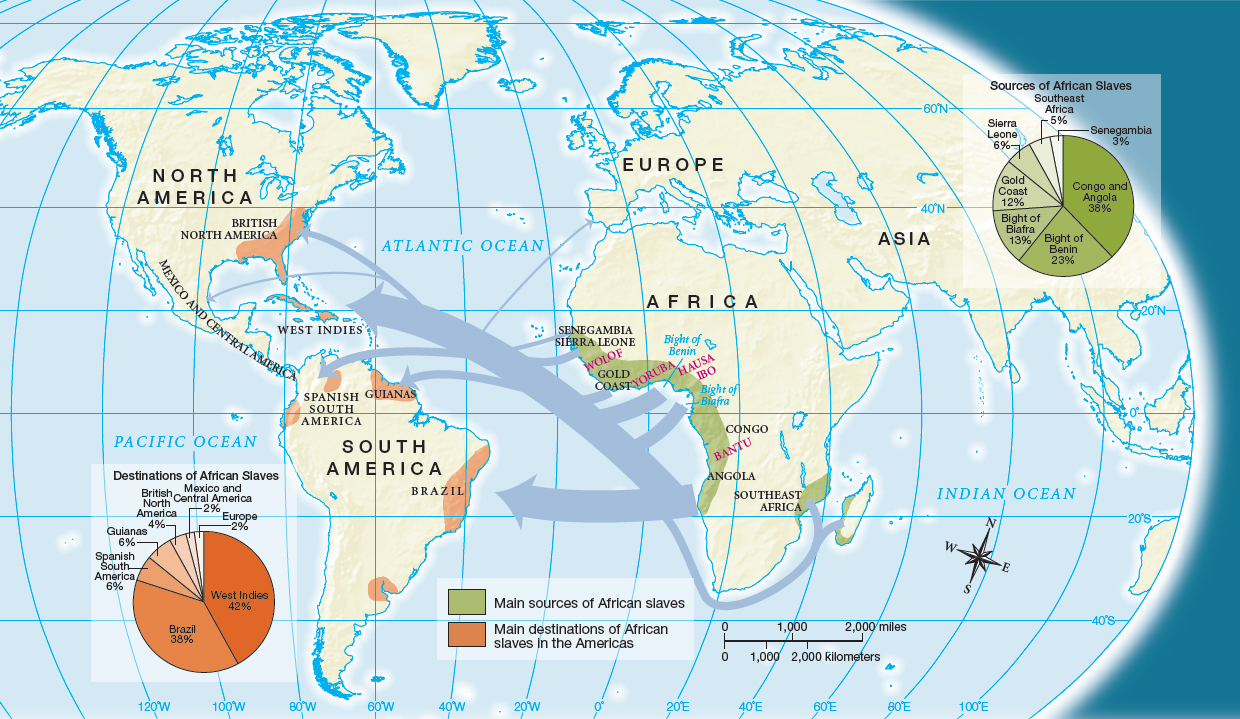
TABLE 5.1 Slave Imports, 1451–1870
Table 5.1 Slave Imports, 1451–1870
| Estimated Slave Imports to the Western Hemisphere | |
| 1451–1600 | 275,000 |
| 1601–1700 | 1,341,000 |
| 1701–1810 | 6,100,000 |
| 1811–1870 | 1,900,000 |
Although they shared African origins, they came from many different cultures. They spoke different languages, worshipped different deities, observed different rules of kinship, grew different crops, and recognized different rulers. The most important experience they had in common was enslavement.

Captured in war, kidnapped, or sold into slavery by other Africans, they were brought to the coast, sold to African traders who assembled slaves for resale, and sold again to European or colonial slave traders or ship captains, who packed two hundred to three hundred or more aboard ships that carried them on the Middle Passage across the Atlantic and then sold them yet again to colonial slave merchants or southern planters.
 The crossing of the Atlantic by slave ships traveling from West Africa to the Americas. Slaves were crowded together in extremely unhealthful circumstances, and mortality rates were high.
The crossing of the Atlantic by slave ships traveling from West Africa to the Americas. Slaves were crowded together in extremely unhealthful circumstances, and mortality rates were high.
Olaudah Equiano published an account of his enslavement that hints at the common experiences of millions of other Africans swept up in the slave trade. When he was eleven years old, Equiano was kidnapped by Africans in what is now Nigeria, who sold him to other Africans, who in turn eventually sold him to a slave ship on the coast. Equiano feared that he was “going to be killed” and “eaten by those white men with horrible looks, red faces, and loose hair.” Once the ship set sail, many of the slaves, crowded together in suffocating heat fouled by filth of all descriptions, died from sickness. “The shrieks of the women and the groans of the dying rendered the whole a scene of horror almost inconceivable,” Equiano recalled. Most of the slaves on the ship were sold in Barbados, but Equiano and some others were shipped off to Virginia, where he “saw few or none of our native Africans and not one soul who could talk to me.” Equiano felt isolated and “exceedingly miserable” because he “had no person to speak to that I could understand.” Finally, the captain of a tobacco ship bound for England purchased Equiano, and he traveled as a slave between North America, England, and the West Indies for ten years until he succeeded in buying his freedom in 1766.
CHAPTER LOCATOR
How did the North American colonies change in the eighteenth century?
What changed in New England life and culture?
What spurred the growth of the middle colonies?
Why did slavery become the defining feature of the southern colonies?
What experiences tended to unify colonists in British North America?
Conclusion: What was the dual identity of British North American colonists?
 LearningCurve
LearningCurve
Check what you know.
The Deadly Middle Passage
> The Deadly Middle Passage
- Eighty-five percent of slaves to the southern colonies came directly from Africa.
- Mortality during the Middle Passage varied considerably from ship to ship.
- On average, about 15 percent of the slaves died.
- In general, the longer the voyage lasted, the more people died.
- Smallpox, dysentery, and acute dehydration were leading causes of death.
- Men outnumbered women two to one.
- Children usually accounted for no more than 10 to 15 percent of the cargo.
Normally, an individual planter purchased at any one time a relatively small number of newly arrived Africans, or new Negroes, as they were called. New Negroes were often profoundly depressed, demoralized, and disoriented. Planters expected their other slaves — either those born into slavery in the colonies (often called country-born or creole slaves) or Africans who had arrived earlier — to help new Negroes become accustomed to their strange new surroundings. Although slaves spoke many different languages, enough linguistic and cultural similarities existed that they could usually communicate with other Africans from the same region.
 Term given to newly arrived African slaves in the colonies. Planters usually maintained only a small number of recent arrivals among their slaves at any given time in order to accelerate their acculturation to their new circumstances.
Term given to newly arrived African slaves in the colonies. Planters usually maintained only a small number of recent arrivals among their slaves at any given time in order to accelerate their acculturation to their new circumstances.
New Africans had to adjust to the physical as well as the cultural environment of the southern colonies. Slaves who had just endured the Middle Passage were poorly nourished, weak, and sick. In this vulnerable state, they encountered the alien diseases of North America without having developed a biological arsenal of acquired immunities. As many as 10 to 15 percent of newly arrived Africans died during their first year in the southern colonies. Nonetheless, the large number of newly enslaved Africans made the influence of African culture in the South stronger in the eighteenth century than ever before — or since.
While newly enslaved Africans poured into the southern colonies, slave mothers bore children, which caused the slave population in the South to grow rapidly. Slave owners encouraged these births. Thomas Jefferson explained, “I consider the labor of a breeding [slave] woman as no object, that a [slave] child raised every 2 years is of more profit than the crop of the best laboring [slave] man.” Although slave mothers loved and nurtured their children, the mortality rate among slave children was high, and the ever-present risk of being separated by sale brought grief to many slave families. Nonetheless, the growing number of slave babies set the southern colonies apart from other New World slave societies, where mortality rates were so high that deaths exceeded births. The high rate of natural increase in the southern colonies meant that by the 1740s the majority of southern slaves were country-born.