Defining America’s Place in a New World Order

In 1991, President George H. W. Bush declared a “new world order” emerging from the ashes of the Cold War. As the sole superpower, the United States was determined to let no nation challenge its military superiority or global leadership: It spent ten times more on defense than its nearest competitor, the United Kingdom (Figure 31.2). Defining principles for the use of that power in a post–Cold War world remained a challenge. [[LP Figure: F31.02 Global Comparison: Countries with the Highest Military Expenditures, 2005/
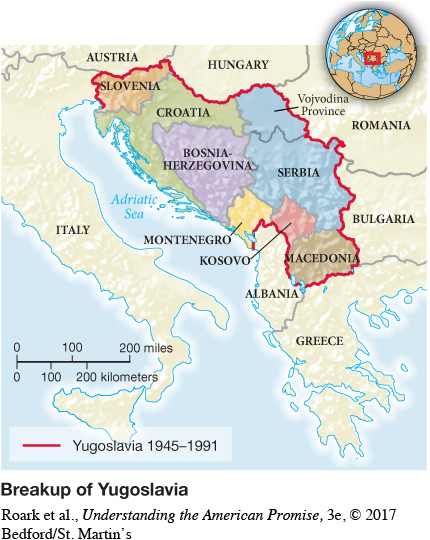
Africa, where civil wars and extreme human suffering rarely evoked a strong U.S. response, was a case in point. In 1992, President Bush had attached U.S. forces to a UN operation in the northern African country of Somalia, where famine and civil war raged. In 1993, President Clinton allowed that humanitarian mission to turn into “nation building”—an effort to establish a stable government—and eighteen U.S. soldiers were killed. The outcry after Americans saw film of a soldier’s corpse dragged through the streets suggested that most citizens were unwilling to sacrifice lives when no vital interest was threatened. Indeed, both the United States and the UN stood by in 1994 when more than half a million people were massacred in a brutal civil war in Rwanda. [[LP Spot Map: SM31.01 Breakup of Yugoslavia/
In Eastern Europe, the collapse of communism ignited a severe crisis when, after the Communists were swept out of power in Yugoslavia in 1989, ruthless leaders exploited ethnic differences to bolster their power. Yugoslavia splintered into separate states and fell into civil war. The Serbian aggression under President Slobodan Milosevic against Bosnian Muslims, which included rape, torture, and mass killings, horrified much of the world, but European and U.S. leaders hesitated to use military force. Finally, in 1995, Clinton ordered U.S. fliers to join NATO forces in intensive bombing of Serbian military concentrations. That effort and successful offensives by the Croatian and Bosnian armies forced Milosevic to the bargaining table, where representatives from Serbia, Croatia, and Bosnia hammered out a peace treaty.
In 1998, new fighting broke out in the southern Serbian province of Kosovo, where ethnic Albanians, who constituted 90 percent of the population, demanded independence. When the Serbian army retaliated, in 1999, NATO launched a U.S.-led bombing attack on Serbian military and government targets that, after three months, forced Milosevic to agree to a settlement. Serbians voted Milosevic out of office in 2000, and he died in 2006 while on trial for genocide by a UN war crimes tribunal.
Elsewhere, Clinton deployed U.S. power when he could send missiles rather than soldiers, and he was prepared to act without international support or UN sanction. In August 1998, bombings at the U.S. embassies in Kenya and Tanzania killed 12 Americans and more than 250 Africans. Clinton retaliated with missile attacks on training camps in Afghanistan and facilities in Sudan controlled by Osama bin Laden, a Saudi-born millionaire who financed Al Qaeda, the Islamic-extremist terrorist network linked to the embassy attacks. Clinton also bombed Iraq in 1993 when a plot to assassinate former president Bush was uncovered, in 1996 after Saddam Hussein attacked the Kurds in northern Iraq, and repeatedly between 1998 and 2000 after Hussein expelled UN weapons inspectors. Whereas Bush had acted in the Gulf War with the support of an international force that included Arab states, Clinton acted unilaterally and in the face of Arab opposition.
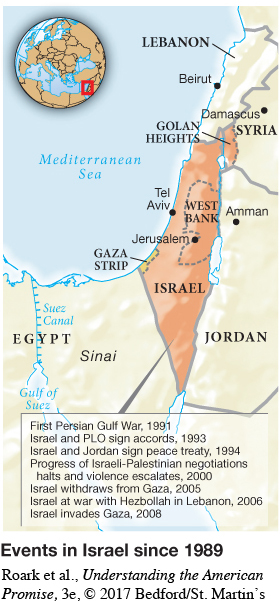
To defuse the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, Clinton applied diplomatic rather than military power. In 1993, Norwegian diplomats had brokered an agreement between Yasir Arafat, head of the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), and Yitzhak Rabin, Israeli prime minister, to recognize the existence of each other’s states. Israel agreed to withdraw from the Gaza Strip and Jericho, allowing for Palestinian self-government there. In July 1994, Clinton presided over another turning point as Israel and Jordan signed a declaration of peace. Yet difficult issues remained, especially control of Jerusalem and the presence of more than 200,000 Israeli settlers in the West Bank, the land seized by Israel in 1967, where three million Palestinians were determined to establish their own state. [[LP Spot Map: SM31.02 Events in Israel since 1989/
Understanding the American Promise 3ePrinted Page 897
Section Chronology