Noun clauses.
Noun clauses. Noun clauses can function as subjects, direct objects, subject complements, or objects of prepositions. A noun clause is always contained within another clause. Noun clauses usually begin with a relative pronoun (that, which, what, who, whom, whose, whatever, whoever, whomever, whichever) or with when, where, whether, why, or how.

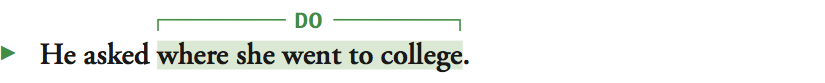


Notice that in each of these sentences the noun clause is an integral part of the independent clause that makes up the sentence. For example, in the second sentence, the independent clause is not just he asked but he asked where she went to college.