49c Create MLA in-text citations.
MLA style requires a citation in the text of a writing project for every quotation, paraphrase, summary, or other material requiring documentation (see 15f). In-text citations document material from other sources with both signal phrases and parenthetical references. Parenthetical references should include the information your readers need to locate the full reference in the list of works cited at the end of the text. An in-text citation in MLA style gives the reader two kinds of information: (1) it indicates which source on the works-cited page the writer is referring to, and (2) it explains where in the source the material quoted, paraphrased, or summarized can be found, if the source has page numbers or other numbered sections.
The basic MLA in-text citation includes the author’s last name either in a signal phrase introducing the source material (see 15b) or in parentheses at the end of the sentence. For print sources, it also includes the page number in parentheses at the end of the sentence.
sample citation using a signal phrase
In his discussion of Monty Python routines, Crystal notes that the group relished “breaking the normal rules” of language (107).
sample parenthetical citation
A noted linguist explains that Monty Python humor often relied on “bizarre linguistic interactions” (Crystal 108).
(For digital sources without print page numbers, see model 3.)
Note in the following examples where punctuation is placed in relation to the parentheses.
1. author named in a signal phrase.The MLA recommends using the author’s name in a signal phrase to introduce the material and citing the page number(s) in parentheses.
Lee claims that his comic-book creation, Thor, was “the first regularly published superhero to speak in a consistently archaic manner” (199).
2. author named in a parenthetical reference. When you do not mention the author in a signal phrase, include the author’s last name before the page number(s) in the parentheses. Use no punctuation between the author’s name and the page number(s).
The word Bollywood is sometimes considered an insult because it implies that Indian movies are merely “a derivative of the American film industry” (Chopra 9).
3. digital or nonprint source. Give enough information in a signal phrase or in parentheses for readers to locate the source in your list of works cited. Many works found online or in electronic databases lack stable page numbers; you can omit the page number in such cases. However, if you are citing a work with stable pagination, such as an article in PDF format, include the page number in parentheses.
digital source without stable page numbers
As a Slate analysis explains, “Prominent sports psychologists get praised for their successes and don’t get grief for their failures” (Engber).
digital source with stable page numbers
According to Whitmarsh, the British military had experimented with using balloons for observation as far back as 1879 (328).
If the source includes numbered sections, paragraphs, or screens, include the abbreviation (sec.), paragraph (par.), or screen (scr.) number in parentheses.
4. two or three authors. Use all the authors’ last names in a signal phrase or in parentheses.
Gortner, Hebrun, and Nicolson maintain that “opinion leaders” influence other people in an organization because they are respected, not because they hold high positions (175).
5. four or more authors. Name all the authors in a signal phrase or in parentheses, or use the first author’s name and et al. (“and others”).
Similarly, as Belenky, Clinchy, Tarule, and Goldberger assert, examining the lives of women expands our understanding of human development (7).
Similarly, as Belenky et al. assert, examining the lives of women expands our understanding of human development (7).
6. organization as author. Provide the group’s full name or a shortened form of it in a signal phrase or in parentheses.
Any study of social welfare involves a close analysis of “the impacts, the benefits, and the costs” of its policies (Social Research Corporation iii).
7. unknown author. Give the full title, if it is brief, in your text—or a shortened version of the title in parentheses.
One analysis defines hype as “an artificially engendered atmosphere of hysteria” (Today’s Marketplace 51).
8. author of two or more works cited in the same project. If your list of works cited has more than one work by the same author, include a shortened version of the title of the work you are citing in a signal phrase or in parentheses to prevent reader confusion.
Gardner shows readers their own silliness in his description of a “pointless, ridiculous monster, crouched in the shadows, stinking of dead men, murdered children, and martyred cows” (Grendel 2).
9. two or more authors with the same last name. Include the author’s first and last names in a signal phrase or first initial and last name in a parenthetical reference.
Children will learn to write if they are allowed to choose their own subjects, James Britton asserts, citing the Schools Council study of the 1960s (37-42).
10. multivolume work. In a parenthetical reference, note the volume number first and then the page number(s), with a colon and one space between them.
Modernist writers prized experimentation and gradually even sought to blur the line between poetry and prose, according to Forster (3: 150).
If you name only one volume of the work in your list of works cited, include only the page number in the parentheses.
11. literary work. Because literary works are often available in many different editions, cite the page number(s) from the edition you used followed by a semicolon, and then give other identifying information that will lead readers to the passage in any edition. Indicate the act and/or scene in a play (37; sc. 1). For a novel, indicate the part or chapter (175; ch. 4).
In utter despair, Dostoyevsky’s character Mitya wonders aloud about the “terrible tragedies realism inflicts on people” (376; bk. 8, ch. 2).
For a poem, cite the part (if there is one) and line(s), separated by a period. If you are citing only line numbers, use the word line(s) in the first reference (lines 33-34).
Whitman speculates, “All goes onward and outward, nothing collapses, / And to die is different from what anyone supposed, and luckier” (6.129-30).
For a verse play, give only the act, scene, and line numbers, separated by periods.
The witches greet Banquo as “Lesser than Macbeth, and greater” (1.3.65).
12. work in an anthology or a collection. For an essay, a short story, or other piece of prose reprinted in an anthology, use the name of the author of the work, not the editor of the anthology, but use the page number(s) from the anthology.
Narratives of captivity play a major role in early writing by women in the United States, as demonstrated by Silko (219).
13. sacred text. To cite a sacred text such as the Qur’an or the Bible, give the title of the edition you used, the book, and the chapter and verse (or their equivalent) separated by a period. In your text, spell out the names of books. In parenthetical references, use abbreviations for books with names of five or more letters (Gen. for Genesis).
He ignored the admonition “Pride goes before destruction, and a haughty spirit before a fall” (New Oxford Annotated Bible, Prov. 16.18).
14. encyclopedia or dictionary entry. An entry from a reference work—such as an encyclopedia or a dictionary—without an author will appear on the works-cited list under the entry’s title. Enclose the entry title in quotation marks, and place it in parentheses. Omit the page number for print reference works that arrange entries alphabetically.
The term prion was coined by Stanley B. Prusiner from the words proteinaceous and infectious and a suffix meaning particle (“Prion”).
15. government source with no author named. Because entries for sources authored by government agencies will appear on your list of works cited under the name of the country (see 49d, item 73), your in-text citation for such a source should include the name of the country as well as the name of the agency responsible for the source.
To reduce the agricultural runoff into the Chesapeake Bay, the United States Environmental Protection Agency has argued that “[h]igh nutrient loading crops, such as corn and soybean, should be replaced with alternatives in environmentally sensitive areas” (2-26).
16. entire work. Include the reference in the text, without any page numbers.
Jon Krakauer’s Into the Wild both criticizes and admires the solitary impulses of its young hero, which end up killing him.
17. indirect source (author quoting someone else). Use the abbreviation qtd. in to indicate that you are quoting from someone else’s report of a source.
As Arthur Miller says, “When somebody is destroyed everybody finally contributes to it, but in Willy’s case, the end product would be virtually the same” (qtd. in Martin and Meyer 375).
18. two or more sources in one parenthetical reference. Separate the information with semicolons.
Economists recommend that employment be redefined to include unpaid domestic labor (Clark 148; Nevins 39).
19. visual included in the text. When you include an image in your text, number it and include a parenthetical reference in your text (see Fig. 2). Number figures (photos, drawings, cartoons, maps, graphs, and charts) and tables separately. Each visual should include a caption with the figure or table number and information about the source—either a complete citation or enough information to direct readers to your works-cited entry. (See 8d and 15c.)
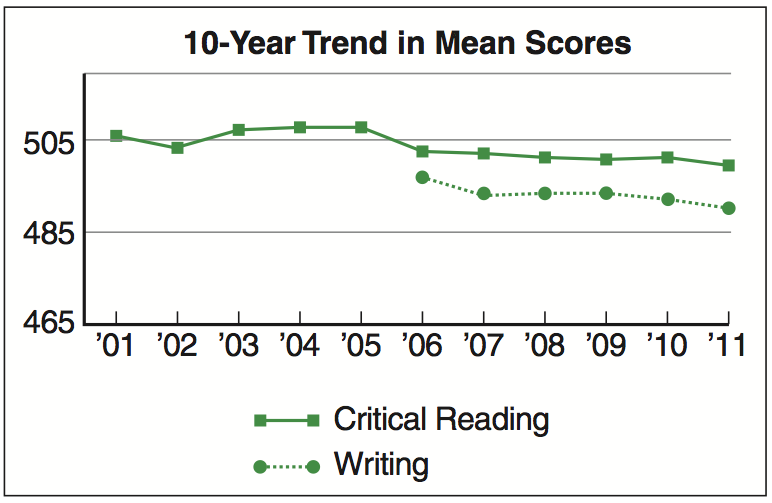
This trend is illustrated in a chart distributed by the College Board as part of its 2011 analysis of aggregate SAT data (see Fig. 1).
Soon after the preceding sentence, readers find the following figure and a caption referring them to the entry on the list of works cited (see 49e and the integrated media page at bedfordstmartins.com/wia to read the student’s research paper):
An image that you create might appear with a caption like this:
Fig. 4. Young women reading magazines. Personal photograph by author.