Chapter 1. Section 6(18), Problem 5
Step 1
Question
Use the market for loanable funds shown in the accompanying diagram to explain what happens to private savings, private investment spending, and the interest rate if each of the following events occur. Assume that there are no capital inflows or outflows.
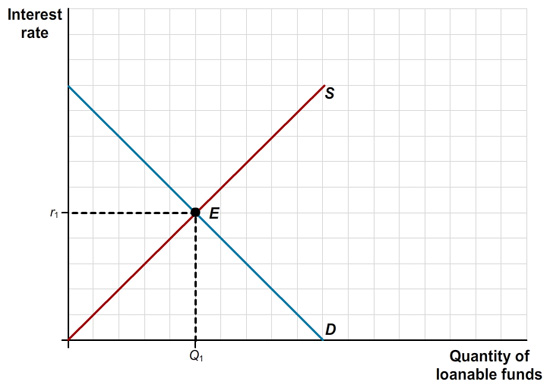
a. If the government reduces the size of its deficit to zero there will be a(n) ihyXI3vweKBVkqtuOIeAYqcmI9iXy7Xh in the ydtncxPy4jWPZjitV933hu/nI3I= of loanable funds. Reducing deficits to zero will cause interest rates to u/Bo3/Gu/P09VZ6/Dkn0NQ==.
Question
Use the market for loanable funds shown in the accompanying diagram to explain what happens to private savings, private investment spending, and the interest rate if each of the following events occur. Assume that there are no capital inflows or outflows.

b. At any given interest rate, if consumers decide to save more and the government budget remains unchanged there will be a(n) Z5/pDly332AjV3TKqM8FMDiwwqSIBbJS in the PuLKO2w5dBBF8OuAiN09YfUEOv8= of loanable funds. This will cause the interest rate to u/Bo3/Gu/P09VZ6/Dkn0NQ==.
Question
Use the market for loanable funds shown in the accompanying diagram to explain what happens to private savings, private investment spending, and the interest rate if each of the following events occur. Assume that there are no capital inflows or outflows.

c. At any given interest rate, if businesses become very optimistic about the future profitability of investment spending and the government budget remains unchanged then the Glw+rSDuFZhvxn7epPgdMM0oWlU= of loanable funds will Z5/pDly332AjV3TKqM8FMDiwwqSIBbJS. This will cause interest rates to TuJN6iTS2KGBP4jBi/sn7g==.