Question 1 of 3
Step 1
Consider the economy of Wiknam.
The consumption function is given by
C = 200 + 0.75(Y – T).
The investment function is
I = 200 – 25r.
Government purchases and taxes are both 100. For this economy, choose the correct graph of the IS curve for r ranging from 0 to 8.

The money demand function in Wiknam is
(M/P)d = Y – 100r.
The money supply M is 1,000 and the price level P is 2. Choose the correct graph of the LM curve for r ranging from 0 to 8.
Find the equilibrium interest rate, r, and the equilibrium level of income Y.
The equilibrium interest rate, r, = %
The equilibrium level of income, Y, =
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
Step 2
Consider the economy of Wiknam.
Suppose that government purchases are increased from 100 to 150. How does the IS curve shift? What are the new equilibrium interest rate and level of income? (Hint: You will need to draw this graphically to answer these questions.)
The IS curve shifts to the by .
The equilibrium interest rate, r, = %.
The equilibrium level of income, Y, = .
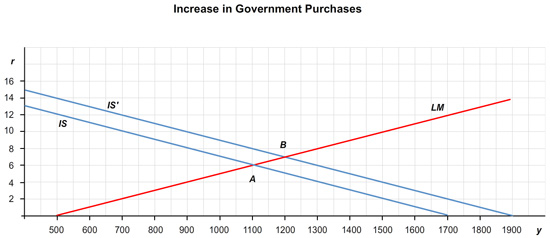
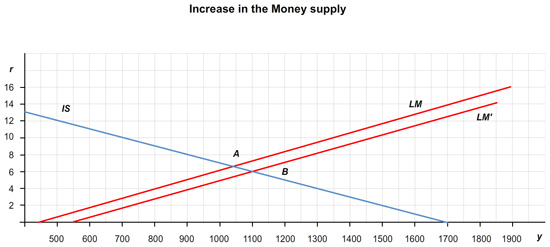
Suppose instead that the money supply is increased from 1,000 to 1,200. How does the LM curve shift? What are the new equilibrium interest rate and level of income? (Hint: You will need to draw this graphically to answer these questions.)
The LM curve shifts to the by .
The equilibrium interest rate, r, = %.
The equilibrium level of income, Y, = .


- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
Step 3
Consider the economy of Wiknam.
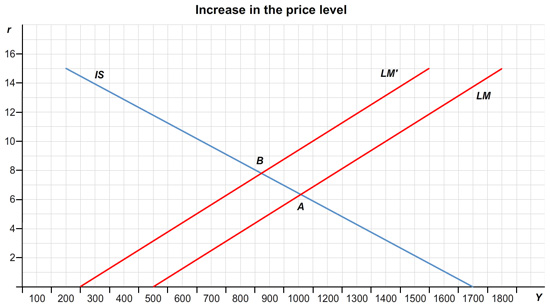
With the initial values for monetary and fiscal policy, suppose that the price level rises from 2 to 4. What happens? What are the new equilibrium interest rate and level of income?
The LM curve shifts to the by as shown in the graph.
The equilibrium interest rate, r, = %
The equilibrium level of income, Y, = .
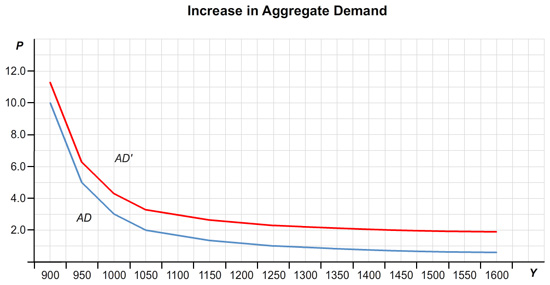
Below is the graph for the aggregate demand curve for the initial values of 1000 for the money supply, 100 for government purchases, and 100 for taxes. What happens to this aggregate demand curve if fiscal or monetary policy changes, as in parts (d) and (e)?
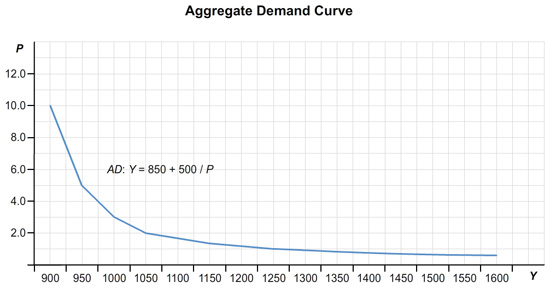
An increase in government purchases will shift the aggregate demand curve to the . An increase in the money supply will shift the aggregate demand curve to the .

- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.