Question 1 of 2
Step 1
Suppose that the money demand function is
(M/P)d= 1,000 – 100r,
where r is the interest rate in percent. The money supply M is 1,000 and the price level P is fixed at 2.
a & b. Below is the graph of supply and demand for real money balances.
What is the equilibrium interest rate?
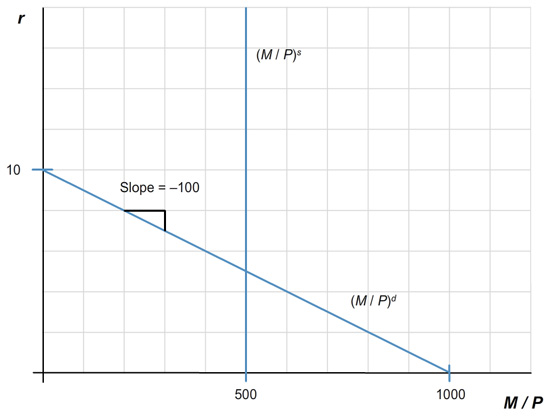
The equilibrium interest rate, r, equals %.
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
Step 2
Suppose that the money demand function is
(M/P)d= 1,000 – 100r,
where r is the interest rate in percent. The money supply M is 1,000 and the price level P is fixed at 2.
c. What happens to the equilibrium interest rate if the supply of money is raised from 1,000 to 1,200?
The equilibrium interest rate, r, equals %.
d. If the central bank wants the interest rate to be 7 percent, what money supply should it set?
The central bank should set the money supply equal to
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.