Question 1 of 3
Step 1
Country A and country B both have the production function
Y = F(K, L) = K1/2L1/2.
Does this production function have constant returns to scale?
What is the per‑worker production function, y = f(k)?
The per-worker production function is _______.
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
Step 2
Country A and country B both have the production function
Y = F(K, L) = K1/2L1/2.
Assume that neither country experiences population growth or technological progress and that 5 percent of capital depreciates each year. Assume further that country A saves 10 percent of output each year and country B saves 20 percent of output each year. Using your answer from part (b) and the steady-state condition that investment equals depreciation, find the steady-state level of capital per worker for each country. Then find the steady-state levels of income per worker and consumption per worker.
Country A:
k* =
y* =
c* =
Country B:
k* =
y* =
c* =
- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.
Step 3
Country A and country B both have the production function
Y = F(K, L) = K1/2L1/2.
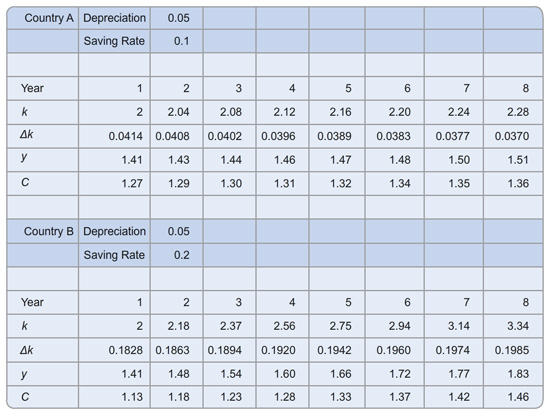
Suppose that both countries start off with a capital stock per worker of 2. What are the levels of income per worker and consumption per worker? Round your answers to two decimal places.
Country A:
y =
c =
Country B:
y =
c =

- Chapters
- descriptions off, selected
- captions settings, opens captions settings dialog
- captions off, selected
- English Captions
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
This is a modal window.