Chapter 2. Analyzing Enzymes and Enzyme Kinetics II
Learning Objectives
General Purpose
Conceptual
- Be able to relate changes in different factors to changes in the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
- Be able to design and conduct experiments to test your hypotheses.
General Purpose
The pre-lab is to prepare for the upcoming experiment procedures you will do during this laboratory. At the end of the last laboratory your instructor described in general terms the various treatments which groups will use in this laboratory. Your group selected one of those treatments and you now need to plan the details of your experiment. Before coming to lab you should write out the complete procedure that you are going to use in your laboratory notebook. Your group should be prepared to review your procedure with your laboratory instructor. If you have questions or are uncertain about your procedure, please check it with your laboratory instructor prior to beginning your experiment. This will save you the time of having to repeat the experiment.
You should be as specific as possible about the details of your procedure (volumes, temperatures, pH, etc.). Unless instructed differently by your instructor, all of the reactions will run for the same length of time (three minutes). The general outlines for the various treatments will be available on each bench during your laboratory. Read each of the procedures to become familiar with the scope of the various experiments and then use the one that is specific for the treatment your group chose as a guide to write your specific procedure.
Procedure Outlines
1. Enzyme Concentration (Work in groups of 2)
Prepare a dilution series of the potato extract containing catecholase provided by your instructor by adjusting the amount of water in each tube. The maximum dilution should be 1/4 of the original strength. The total volume in each cuvette should be 9 mL, and the volume of catechol should be 5 mL. Adjust the volume of potato extract and the dH2O for each treatment. If you are investigating the rate of the reaction when the potato extract containing catecholase is diluted by one half, each experimental tube will contain 3.5 mL of water, 5 mL of 0.05 M catechol, and 0.5 mL of the potato extract containing catecholase. Note that the total volume is 9 mL. The blank will contain 8.5 mL of water and 0.5 mL of the potato extract containing catecholase. The volumes for the components are shown in Table 3-1 below.
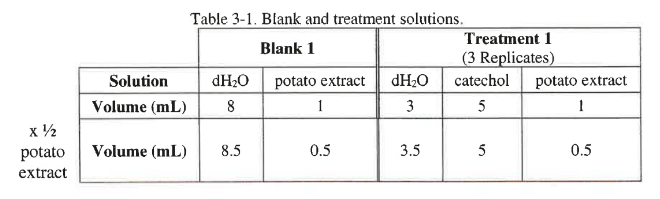
Complete the dilution series using different concentrations for treatments 2 and 3 create the tables forall 3 treatments in your lab notebook. You will need to prepare a "blank solution" for each dilution, so don’t forget to include the appropriate volumes of water or enzyme in the blank. You can use table 3-2 as a guide for the construction of your tables in your lab notebook.
You will measure the absorbance every 30 seconds over a three-minute period. To record the data construct a table in your lab notebook similar to the example shown in table 3-3.
The color of each of the reaction solutions will also be observed and recorded. To record those observations construct a table in your lab notebook similar to the example shown in table 3-4.
2. Substrate Concentration (Work in groups of 2)
Prepare a dilution series of 0.05 M catechol by adjusting the amount of water in each tube. The total volume in each cuvette should be 9 mL, and the volume of potato extract should be 1 mL. Adjust the volume of 0.05 M catechol and the dH2O for each treatment. If you are investigating the rate of the reaction when the catechol substrate is diluted by one half, each experimental tube will contain 5.5 mL of water, 2.5 mL of 0.05 M catechol, and 1 mL of the potato extract containing catecholase. Note that the total volume is 9 mL. The blank will contain 8 mL of water and 1 mL of the potato extract containing catecholase. The volumes for the components are shown in Table 3-5 below.
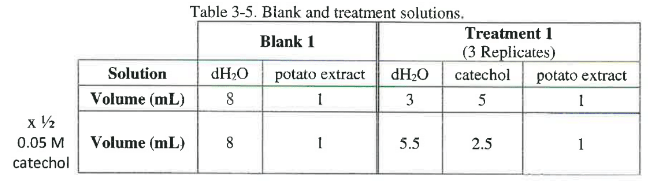
Complete the dilution series using different concentrations for treatments 2 and 3 create the tables for all 3 treatments in your lab notebook. Even though the blank is the same for each you will need to prepare a "blank solution" for each dilution because the potato extract changes over time. You can use table 3-2 as a guide for the construction of your tables in your lab notebook.
You will measure the absorbance every 30 seconds over a three-minute period. To record the data construct a table in your lab notebook similar to the example shown in table 3-3.
The color of each of the reaction solutions will also be observed and recorded. To record those observations construct a table in your lab notebook similar to the example shown in table 3-4.
3. Structure of the Substrate (Work in groups of 2)
There are several structural isomers of catechol. Two of these are resorcinol and hydroquinone (Figure 3-2).
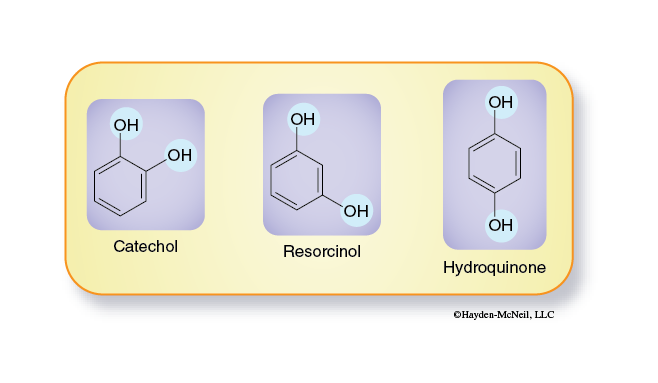
These molecules differ only in the relative positions of the hydroxyl groups. Prepare a series of tubes containing 3 mL of water and 5 mL of one substrate solutions (0.05M catechol, 0.05 M resorcinol, or 0.05 M hydroquinone).
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
The total volume in each cuvette should be 9 mL, and the volume of potato extract should be 1 mL. In the treatments use either 0.05 M catechol or one of the other substrates. The blank will contain 8 mL of water and 1 mL of the potato extract containing catecholase. The volumes for the components are shown in Table 3-6 below.
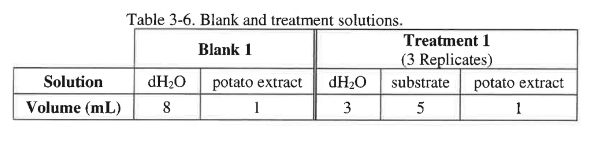
Create the tables for all 3 treatments in your lab notebook. Even though the blank is the same for each you will need to prepare a "blank solution" for each subtrate because the potato extract changes over time. You can use table 3-2 as a guide for the construction of your tables in your lab notebook.
You will measure the absorbance every 30 seconds over a three-minute period. To record the data construct a table in your lab notebook similar to the example shown in table 3-3. The color of each of the reaction solutions will also be observed and recorded. To record those observations construct a table in your lab notebook similar to the example shown in table 3-4.
4. pH (Work in groups of 2)
In the previous experiment the reaction was carried out at using dH2O at a pH of 7. Create a consistent pH series in addition to pH 7 for the other treatments by choosing two other buffers from the following pHs: 3, 5, 9, or 11. The buffers will substitute for the water in the basic reaction. The total volume in each cuvette should be 9 mL, and the volume of potato extract should be 1 mL. The blank will contain 8 mL of water or 8 mL of the appropriate buffer and 1 mL of the potato extract containing catecholase. The volumes for the components are shown in Table 3-7 below.
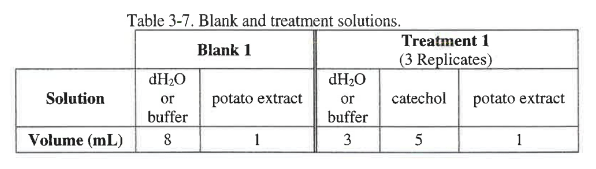
Create the tables for all 3 treatments in your lab notebook. The blank for each treatment should be at the same pH as the treatment so you will need to prepare a "blank solution" for each treatment. You can use table 3-2 as a guide for the construction of your tables in your lab notebook.
You will measure the absorbance every 30 seconds over a three-minute period. To record the data construct a table in your lab notebook similar to the example shown in table 3-3.
5. Temperature (Work in groups of 2)
In the previous experiment the reaction was carried out at room temperature (22-23°C). Create a consistent temperature series in addition to room temperature by choosing two other temperature environments from the following: ice bath (0°C), refrigerator (5°C), water bath (45°C) or water bath (70°C). The total volume in each cuvette should be 9 mL, and the volume of potato extract should be 1 mL. The volumes for the components are shown in Table 3-7 below.

Create the tables for all 3 treatments in your lab notebook. The blank for each treatment should be at the same temperature as the treatment so you will need to prepare a "blank solution" for each treatment. You can use table 3-2 as a guide for the construction of your tables in your lab notebook.
You will measure the absorbance every 30 seconds over a three-minute period. To record the dataconstruct a table in your lab notebook similar to the example shown in table 3-3.
The color of each of the reaction solutions will also be observed and recorded. To record those observations construct a table in your lab notebook similar to the example shown in table 3-4.
6. Source of Enzyme (Work in groups of 2)
In the previous experiment the reaction was carried out using potato extract as the source of the enzyme. There are many other fruits and vegetables which also contain catecholase. Select 2 other sources and bring the material to lab. Prepare the enzyme extract from each of your source materials using the following method:
a. Use a triple beam balance to obtain about 20 g of the enzyme source material (no peel or seeds).
b. Blend the enzyme source material with about 125 mL cold dH2O for two minutes.
c. Use a funnel and two layers of cheese cloth to filter out any particulate matter and collect the extract into a flask.
d. Use the resulting extracts for your 3 treatment (potato enzyme extract and extract from 2 other sources used separately).
The total volume in each cuvette should be 9 mL, and the volume of potato extract should be 1 mL. The volumes for the components are shown in Table 3-8 below.

Create the tables for all 3 treatments in your lab notebook. The blank for each treatment should be made with the same extract source as the treatment so you will need to prepare a "blank solution" for each treatment. You can use table 3-2 as a guide for the construction of your tables in your lab notebook.
You will measure the absorbance every 30 seconds over a three-minute period. To record the data construct a table in your lab notebook similar to the example shown in table 3-3.
The color of each of the reaction solutions will also be observed and recorded. To record those observations construct a table in your lab notebook similar to the example shown in table 3-4.
Pre-Lab Quiz
Proceed to the Pre-Lab Quiz