M2-b: When to use the
The definite article, the, is used with most nouns—both count and noncount—that the reader can identify specifically. Usually the identity will be clear to the reader for one of the following reasons. (See the chart in M2-d.)
- The noun has been previously mentioned.

The article A is used before truck when the noun is first mentioned. When the noun is mentioned again, it needs the article the because readers can now identify which truck skidded—the one that cut in front of the van.
- A phrase or clause following the noun restricts its identity.

The phrase in his car identifies the specific GPS.
note: Descriptive adjectives do not necessarily make a noun specific. A specific noun is one that readers can identify within a group of nouns of the same type.
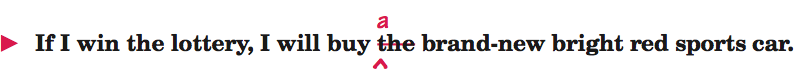
The reader cannot identify which specific brand-new bright red sports car the writer will buy. Even though car has many adjectives in front of it, it is a general noun in this sentence.
- A superlative adjective such as best or most intelligent makes the noun’s identity specific. (See also G4-d.)

The superlative tallest makes the noun boy specific. Although there might be several tall boys, only one boy can be the tallest.
- The noun describes a unique person, place, or thing.

There is only one sun in our solar system, so its identity is clear.
- The context or situation makes the noun’s identity clear.

Both the speaker and the listener know which door is meant.
- The noun is singular and refers to a scientific class or category of items (most often animals, musical instruments, and inventions).

The writer is referring to the tin whistle as a class of musical instruments.
Types of nouns
Common or proper
| Common nouns | Examples | |
| name general persons, places, things, or ideas | religion knowledge rain | beautystudentcountry |
| begin with lowercase |
| Proper nouns | Examples | |
| name specific persons, places, things, or ideas | HinduismPhilip | President AdamsWashington Monument |
| begin with capital letter | New JerseyVietnam | Supreme CourtRenaissance |
Count or noncount (common nouns only)
| Count nouns | Examples | |
| name persons, places, things, or ideas that can be counted | girl, girlscity, citiesgoose, geese | |
| have plural forms | philosophy, philosophies |
| Noncount nouns | Examples | |
| name things or abstract ideas that cannot be counted | watersilverfurniture | patienceknowledgeair |
| cannot be made plural |
note: See the chart in M2-d for lists of commonly used noncount nouns.
Singular or plural (both common and proper)
| Singular nouns(count and noncount) | Examples | |
| represent one person, place, thing, or idea | backpackcountrywomanachievement | rainbeautyNile RiverBlock Island |
| Plural nouns (count only) | Examples | |
| represent more than one person, place, thing, or idea | backpackscountrieswomen | Ural MountainsFalkland Islandsachievements |
| must be count nouns |
Specific (definite) or general (indefinite) (count and noncount)
| Specific nouns | Examples |
| name persons, places, things, or ideas that can be identified within a group of the same type |
The students in Professor Martin’s class should study. The airplane carrying the senator was late. The furniture in the truck was damaged. |
| General nouns | Examples |
| name categories of persons, places, things, or ideas (often plural) |
Students should study. Books bridge gaps between cultures. The airplane has made commuting between cities easy. |