Verb + noun or pronoun + infinitive
Marked infinitive (with to)
With certain verbs in the active voice, a noun or pronoun must come between the verb and the infinitive that follows it. The noun or pronoun usually names a person who is affected by the action.
|
advise |
convince |
order |
tell |
|
allow |
encourage |
persuade |
urge |
|
cause |
have (“own”) |
remind |
warn |
|
command |
instruct |
require |

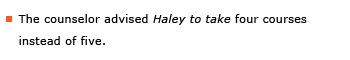

Some verbs may be followed either by an infinitive alone or by a noun or pronoun plus an infinitive:
|
ask |
help |
promise |
would like |
|
expect |
need |
want |


Unmarked infinitive (without to)
An unmarked infinitive is an infinitive without to. A few verbs (often called causative verbs) may be followed by a noun or pronoun and an unmarked infinitive.
|
have (“cause”) |
help |
|
let (“allow”) |
make (“force”) |


NOTE: Help can be followed by a noun or pronoun and either an unmarked or a marked infinitive:

Exercises: