17 | Mixed Constructions and Faulty Predication
17|Mixed Constructions and Faulty Predication
Sometimes a sentence contains all the necessary ingredients but still doesn’t make sense.
17aLink phrases and clauses logically.
A phrase consists of two or more related words that work together but may lack a subject, a verb, or both (see 4b).
A clause is a group of related words that includes both a subject and a verb (see 4a).
A mixed construction results when a writer connects phrases or clauses (or both) that don’t work together as a sentence.
| MIXED | In her efforts to solve the tax problem only caused the mayor additional difficulties. |
A preposition is a transitional word (such as in, on, at, of, from) that leads into a phrase (see 1f).
The prepositional phrase In her efforts to solve the tax problem is a modifier; it can’t act as the subject of a sentence. The writer, however, has used this phrase as a noun—the subject of the verb caused. To untangle this mixed construction, the writer has two choices: (1) rewrite the phrase so that it works as a noun, or (2) use the phrase as a modifier, not as a subject.
| REVISED | Her efforts to solve the tax problem only caused the mayor additional difficulties. [With in gone, efforts becomes the subject.] |
| REVISED | In her efforts to solve the tax problem, the mayor created additional difficulties. [The phrase now modifies the verb created.] |
To fix a mixed construction, check your links—especially prepositions and conjunctions.
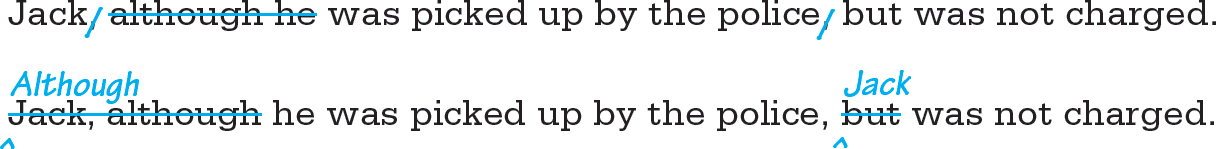
799
For more on coordination and subordination, see 19f.
Coordinating conjunctions join elements with equal or near-equal importance (see 1g and 19a–19c).
A subordinating conjunction is a word (such as because, although, if, when) used to make one clause dependent on, or subordinate to, another (see 1g and 19d–19f).
 Guidelines for Multilingual Writers
Guidelines for Multilingual Writers
How Can I Avoid Mixed Constructions, Faulty Predication, and Subject Errors?
Mixed constructions result when phrases or clauses are joined even though they do not logically go together. Combine clauses with either a coordinating conjunction or a subordinating conjunction, never both.
Although baseball is called “the national pastime” of the United States, but football is probably more popular.

Faulty predication results when a verb and its subject, object, or modifier do not match. Do not use a noun as both the subject of the sentence and the object of a preposition.
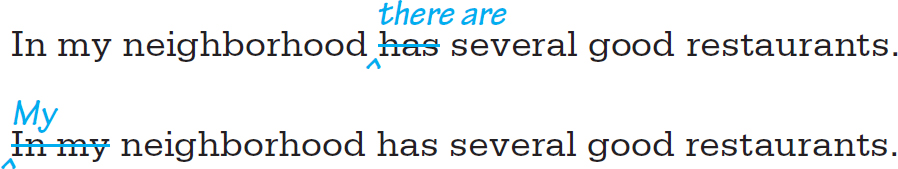
Subject errors include leaving out and repeating subjects of clauses.
Do not omit it used as a subject. A subject is required in all English sentences except commands (imperatives).
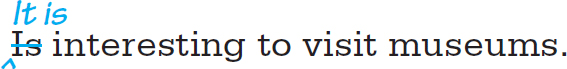
Do not repeat the subject of a sentence with a pronoun.
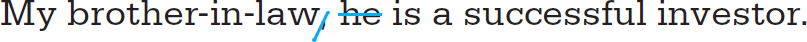
17bRelate the parts of a sentence logically.
A subject is the part of a sentence that names something—a person, an object, an idea, a situation—about which the verb makes an assertion (see 2).
Faulty predication refers to a skewed relationship between a verb and some other part of a sentence.
| FAULTY | The temperature of water freezes at 32 degrees Fahrenheit. |
At first glance, that sentence looks all right. It contains both subject and verb. It expresses a complete thought. What is wrong with it? The writer has mismatched the subject and verb. The sentence tells us that temperature freezes, when science and common sense tell us water freezes. The writer needs to select a subject and verb that fit each other.
A verb is a word that shows action or state of being (see 1c and 3).
| REVISED | Water freezes at 32 degrees Fahrenheit. |
Faulty predication also results from a mismatched verb and direct object.
Costs don’t diminish college. To correct this error, the writer changed the sentence so that its direct object follows logically from its verb. Subtler predication errors result when a writer uses a linking verb to forge a false connection between the subject and a subject complement.
800
A direct object is the target of a verb that completes the action performed by the subject or asserted about the subject (see 3a).
| FAULTY | Industrial waste has become an important modern priority. |
Is it waste that has become a priority? Or is it solving problems caused by careless disposal of industrial waste? A writer who says all that, though, risks wordiness. Why not just replace priority with a closer match for waste?
A linking verb is a verb that shows a state of being by linking the sentence subject with a word that renames or describes the subject (see 1c and 3b).
| REVISED | Industrial waste has become a modern menace. |
Mismatches between a verb and another part of the sentence are easier to avoid when the verb is active rather than passive.
17cAvoid starting a definition with is when or is where.
A definition needs to fit grammatically with the rest of the sentence.
Dyslexia is when you have a reading disorder.
17dAvoid using the reason is because . . .
Anytime you start an explanation with the reason is, what follows is should be a subject complement: an adjective, a noun, or a noun clause. Because is a conjunction; it cannot function as a noun or an adjective.
The reason Al hesitates is because no one supported him last year.
EXERCISE 17-1 Correcting Mixed Constructions and Faulty Predication
Correct any mixed constructions and faulty predication you find in the following sentences. Example:
Or
801
The cost of health insurance protects people from big medical bills.
In his determination to prevail helped him finish the race.
The AIDS epidemic destroys the body’s immune system.
The temperatures are too cold for the orange trees.
A recession is when economic growth is small or nonexistent and unemployment increases.
The opening of the new shopping mall should draw out-of-town shoppers for years to come.
The reason the referendum was defeated was because voters are tired of paying so much in taxes.
In the glacier’s retreat created the valley.
A drop in prices could put farmers out of business.
The researchers’ main goal is cancer.