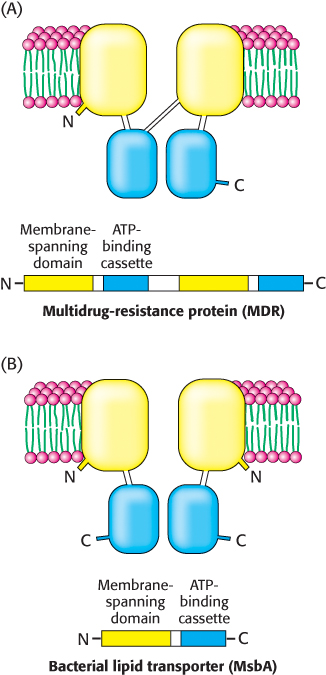
Domain arrangement of ABC transporters. ABC transporters are a large family of homologous proteins composed of two transmembrane domains and two ATP- P- g-