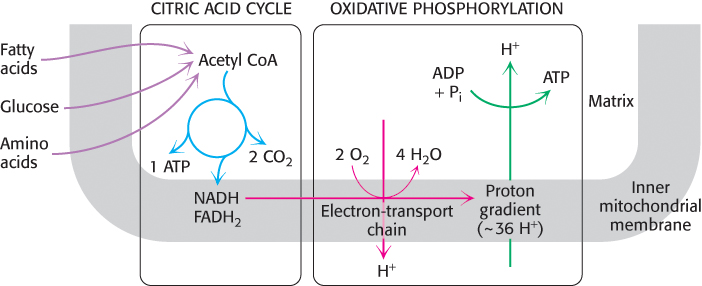
Cellular respiration. The citric acid cycle constitutes the first stage in cellular respiration, the removal of high-