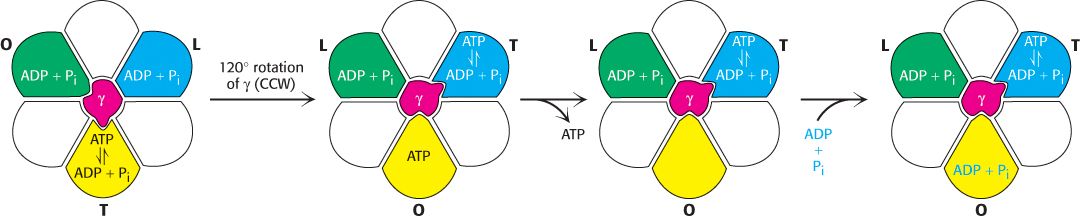
Binding- T- O- 0- L-