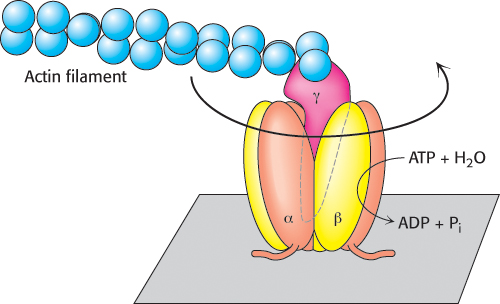
Direct observation of ATP-