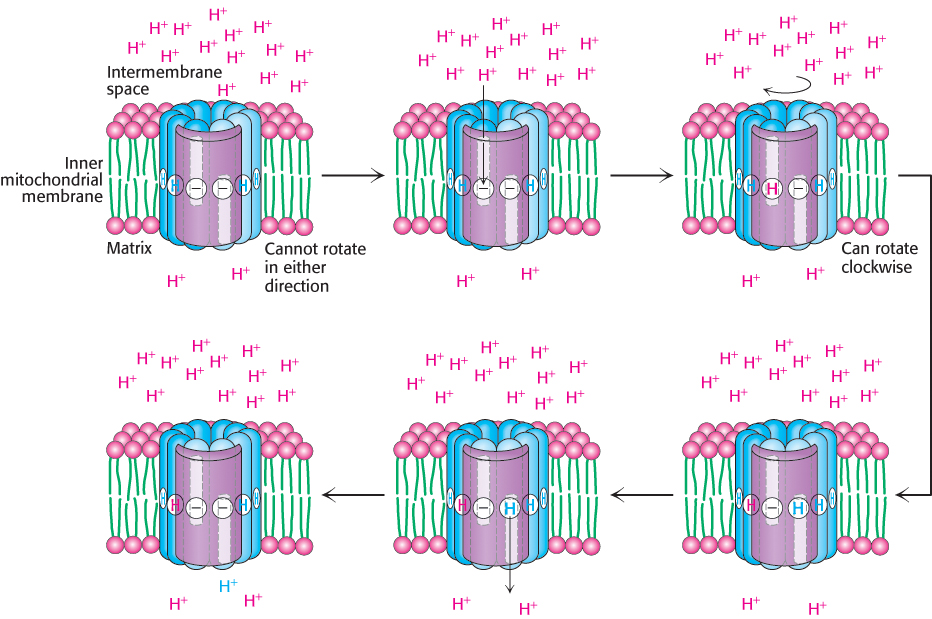
Proton motion across the membrane drives rotation of the c ring. A proton enters from the intermembrane space into the cytoplasmic half- f-