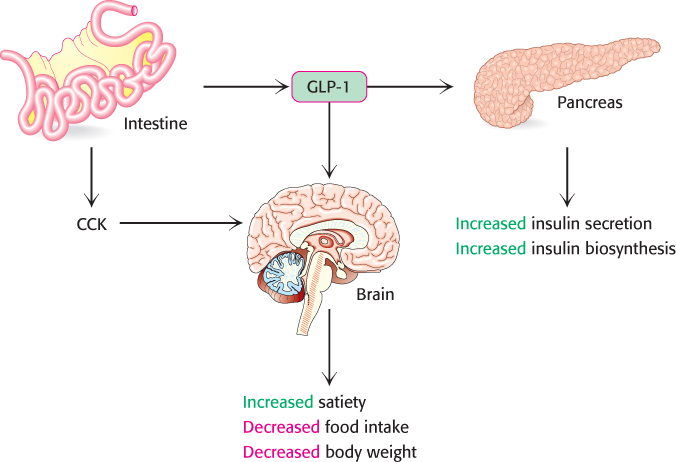
Satiation signals. Cholecystokinin (CCK) and glucagon- P- P-
[Information from S. C. Wood, Cell Metab. 9:489–