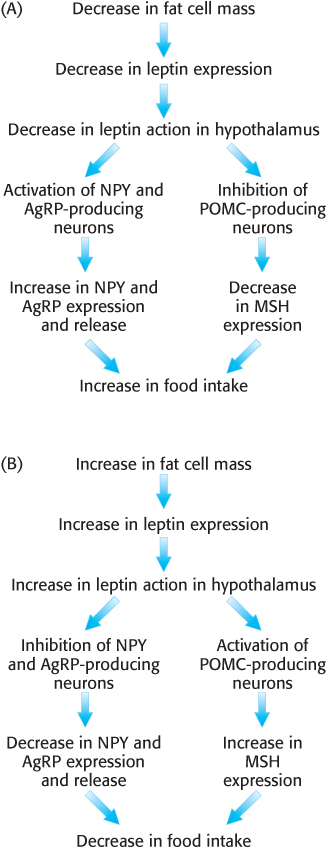
The effects of leptin in the brain. Leptin is an adipokine secreted by adipose tissue in direct relation to fat mass. (A) When leptin levels fall, as in fasting, appetite- e- e-
[Information from M. H. Stipanuk, Biochemical, Physiological, & Molecular Aspects of Human Nutrition, 2d ed. (Saunders/Elsevier, 2006), Fig. 22-