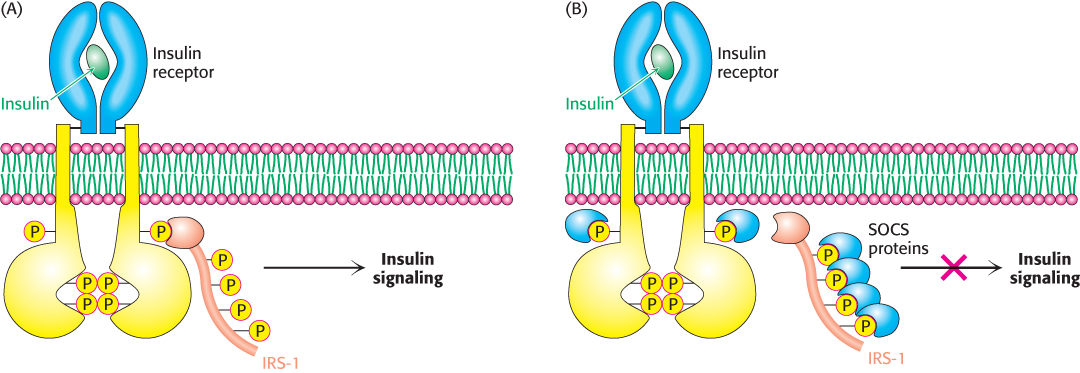
Suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) regulate receptor function. (A) Insulin binding results in phosphorylation of the receptor and subsequent phosphorylation of IRS- n- n- S- n-