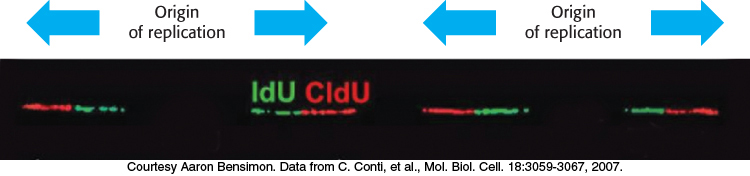
Eukaryotic origins of replication. The image shows a single molecule of DNA containing two origins of replication. The origins were identified by labeling new replicated DNA in human cells first with one thymine analog (iodo- I- o- l- I- l-