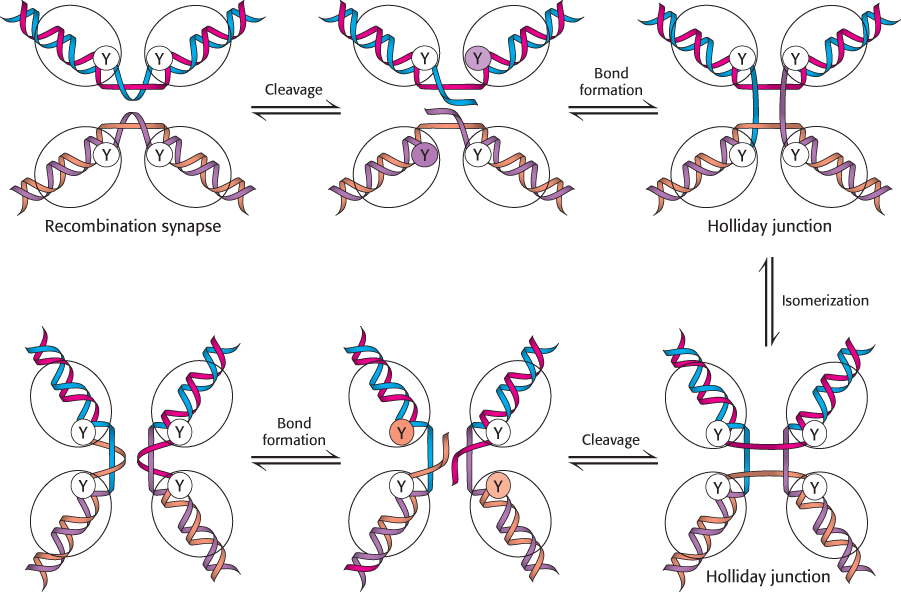
Recombination mechanism. Recombination begins as two DNA molecules come together to form a recombination synapse. One strand from each duplex is cleaved by transesterification with the 3′ end of each of the cleaved strands linked to a tyrosine residue on the recombinase enzyme. New phosphodiester bonds are formed when a 5′ end of the other cleaved strand in the complex attacks these tyrosine–