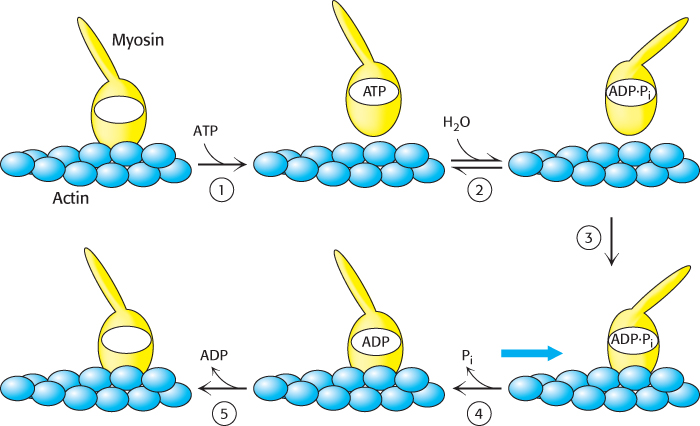
Myosin motion along actin. A myosin head (yellow) in the apo form is bound to an actin filament (blue). The binding of ATP (1) results in the release of myosin from actin. The reversible hydrolysis of ATP bound to myosin (2) can result in the reorientation of the lever arm. With ATP hydrolyzed but still bound to actin, myosin can bind actin (3). The release of Pi (4) results in the reorientation of the lever arm and the concomitant motion of actin relative to myosin. The release of ADP (5) completes the cycle.