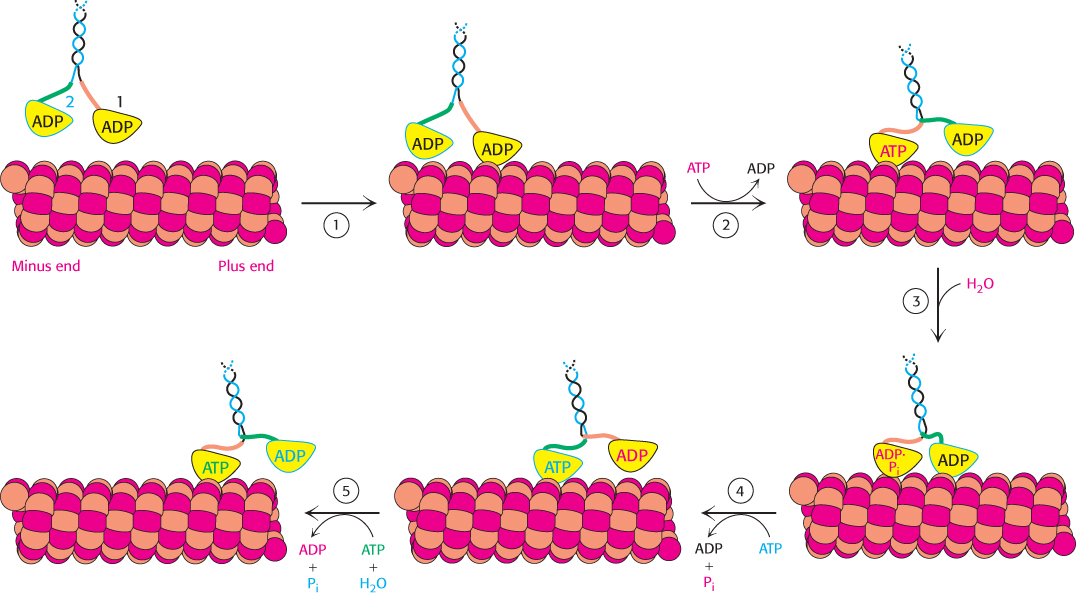
Kinesin moving along a microtubule. (1) One head of a two-