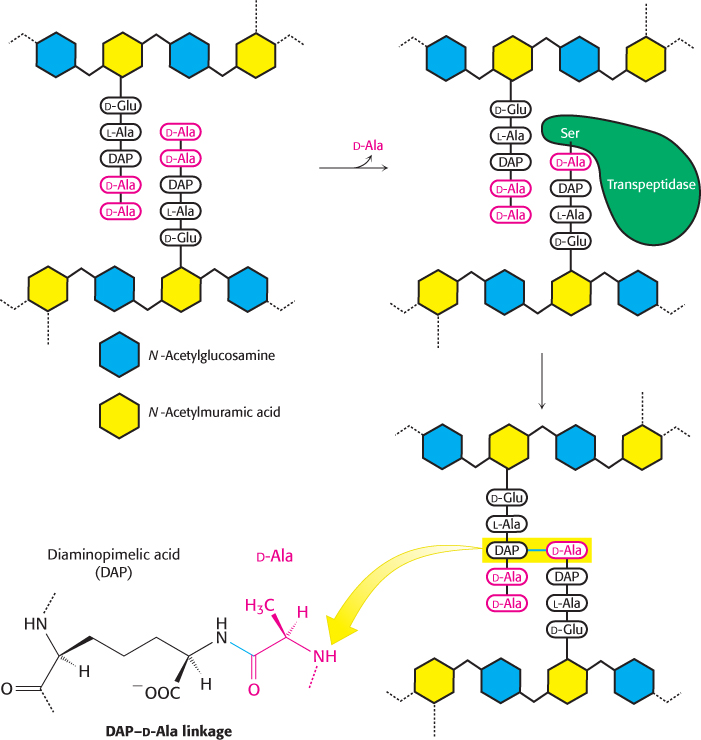
Mechanism of cell- s- m- e- m-