Chapter 33
1. The transgenic nematode would avoid the compound. The identity of the ligand is determined by the receptor, whereas the behavioral response is dictated by the neuron in which the receptor is expressed.
2. Only a mixture of compounds C5-COOH and HOOC-
3. Bitter and sweet sensations are mediated by G proteins coupled to 7TM receptors, leading to millisecond time resolution. Salty and sour sensations are mediated directly by ion channels, which may lead to faster time resolution.
4. Sound travels 0.15 m in 428 µs. The human hearing system is capable of sensing time differences of close to a microsecond, and so the difference in arrival times at the two ears is substantial. A system based on G proteins is unlikely to be able to reliably distinguish between signals arriving at the two ears, because G proteins typically respond in milliseconds.
5. If a plant tastes bitter, animals will avoid eating it even if it is nontoxic, which may provide a selective advantage to the plant.
6. Using mice in which either the gene for T1R1 or the gene for T1R3 has been disrupted, test the taste responses of these mice to glutamate, aspartate, and a wide variety of other amino acids.
7. 530 nm light will be absorbed to some degree by all three photoreceptors, with the largest absorption from the “green” receptor.
8. These women have four functional color receptors: blue, red, green, and a red–
9. 380 (one for each receptor); there are (380 × 379)/2! = 72,010 combinations of two receptors; (380 × 379 × 378)/3! = 9,073,260 combinations of three receptors.
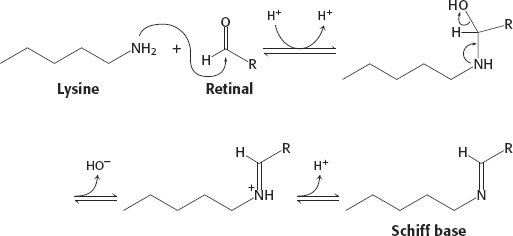
10. The absorption of light converts 11-
11. These compounds are enantiomers and must bind to protein receptors to elicit a smell. Even these subtle structural differences can affect relative receptor binding affinities and, hence, the elicited odor.
12. Vision: cGMP-
A46
13. For all senses, ATP hydrolysis is required to generate and maintain ion gradients and membrane potential. Olfaction: ATP is required for the synthesis of cAMP. Gustation: ATP is required for the synthesis of cyclic nucleotides, and GTP is required for the action of gustducin in the detection of bitter and sweet tastes. Vision: GTP is required for the synthesis of cGMP and for the action of transducin. Hearing and touch: ATP hydrolysis is required to generate and maintain ion gradients and membrane potential and may be required for other roles as well.
14.