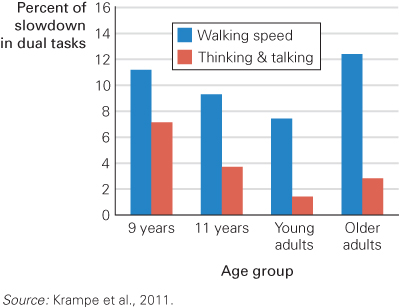
FIGURE 14.3 One Task at a Time Doing two things at once impairs performance. In this study, researchers compared the speed of a sensorimotor task (walking) and a cognitive task (naming objects within a category—for example, colours, spices, insects, crimes, four-legged animals). The participants did each task separately first, and then they did both at once. The latter resulted in performance losses across the board. Note, however, that the eldest seemed to safeguard verbal fluency (only a 3 percent slowdown) at the expense of significantly slower walking.