Type of Signal
communicate via electrical and chemical signals
communicate via chemical signals (hormones)
endocrine
nervous
Signal Transport
transported to target cells by the circulatory system
travel down axons and across synapses to target cells
endocrine
nervous
Target Location
target cells are located at a distance
target cells are located nearby (across the synapse)
endocrine
nervous
Response Time and Duration
responses are generally rapid and short-lived
responses are generally slower and long-lasting
endocrine
nervous
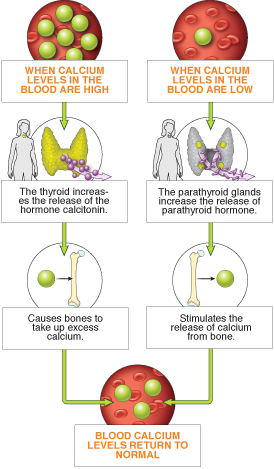
Hormones are chemical signals secreted by cells into the circulatory
system that influence the actions of cells elsewhere in the body. There are
two major types of hormones: steroid hormones and peptide/protein
hormones.
Steroid hormones are synthesized from ________________ ,
whereas peptide/protein hormones are composed of ____________ ____ .
Steroid hormones are synthesized from ________________ ,
whereas peptide/protein hormones are composed of ____________ ____ .
carbohydrates
cholesterol
nucleotides
amino acids

Modes of Action
activate enzymes and other chemical pathways that
can cause many different changes within the target cell
hormone-receptor complex may bind to
DNA and influence gene expression
steroid hormones
peptide/protein hormones
Oxytocin Targets
ADH Target
adrenal glands
parathyroid gland
uterus
brain
kidneys
mammary glands
Oxytocin Functions
ADH Functions
metabolic regulation
milk “let-down”
uterine contractions (during childbirth)
milk production
social attachments
water retention
Hormone
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
luteinizing hormone (LH)
prolactin
adrenocorticotropic hormone
growth hormone
Target
adrenal glands
liver (and other organs)
mammary glands
thyroid gland
ovaries/testes
stimulates release of chemicals important for bone, cartilage, and other tissue growth
stimulates production of thyroxine
triggers ovulation (females)/ stimulates testosterone production (males)
stimulates production of cortisol and other stress-related hormones
stimulates milk production
stimulates follicle development (females) / stimulates sperm maturation (males)
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
growth hormone
prolactin
follicle stimulating hormone
adrenocorticotropic hormone
luteinizing hormone