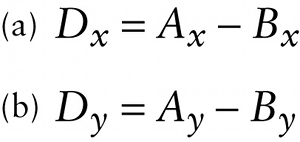Rules for vector subtraction using components (3-4)
Question 1 of 6
Question
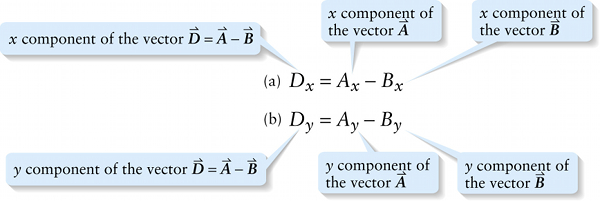
\(x\) component of the vector \(\boldsymbol{\vec{D} = \vec{A} - \vec{B}}\)
{"title":"x component of the vector D = A - B","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"85,26,114,56\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"}]"} {"title":"x component of the vector A","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"178,32,214,52\"}]"} {"title":"x component of the vector B","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"276,26,301,52\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"113,132\"}]"} {"title":"y component of the vector D = A - B","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"75,111,120,144\"}]"} {"title":"y component of the vector A","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#333333","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"178,105,212,139\"}]"} {"title":"y component of the vector B","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#800000","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"259,112,300,137\"}]"}Review
If we subtract \(\boldsymbol{\vec{B}}\) from \(\boldsymbol{\vec{A}}\) to form the vector difference \(\boldsymbol{\vec{D} = \vec{A} - \vec{B} = \vec{A} + (- \vec{B})}\) , each component of \(\boldsymbol{\vec{D}}\) is equal to the sum of the corresponding components of \(\boldsymbol{\vec{A}}\) and \(\boldsymbol{-\vec{B}}\). The components of \(\boldsymbol{-\vec{B}}\) are \(-\vec{B}_x\) and \(-\vec{B}_y\), so the components of \(\boldsymbol{\vec{D}}\) are \(\vec{D}_x = A_x + (-B_x) = A_x - B_x\) and \(D_y = A_y + (-B_y) = A_y - B_y\).