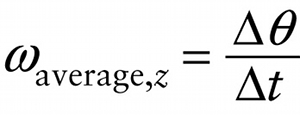Average angular velocity (8-1)
Question 1 of 3
Question
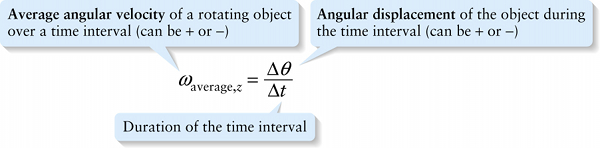
\(\textbf{Average angular velocity}\) of a rotating object over a time interval (can be + or −)
{"title":"Average angular velocity of a rotating object over a time interval (can be + or −)","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"5,39,44,74\"}]"} {"title":"Angular displacement of the object during the time interval (can be + or −)","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"118,11,119,13\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"267,11,298,45\"}]"} {"title":"Duration of the time interval","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"264,72,289,105\"}]"}Review
Here \(\omega\) is the Greek letter omega, and the \(z\) in the subscript tells us that the blade is rotating around an axis that we call the \(z\) axis (Figure 8-3). For any rotating rigid object, the value of \(\omega_\mathrm{average}\), \(z\) is the same for all pieces of the object. The average angular velocity can be positive or negative, depending on the direction in which the object rotates. A common choice is to take counterclockwise rotation to be positive and clockwise rotation to be negative, but the choice is up to you.