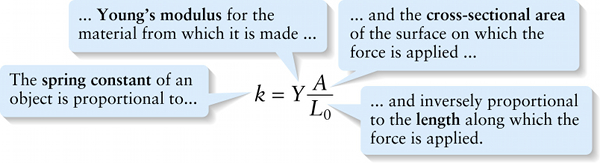
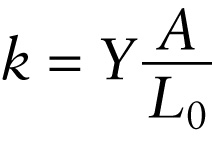Spring constant for an object under tension or compression (9-2)
Question 1 of 4
Question
...and the \(\textbf{cross-sectional area}\) of the surface on which the force is applied ...
{"title":"The spring constant of an object is proportional to...","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"2,34,34,83\"}]"} {"title":"...Young's modulus for the material from which it is made ...","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"118,11,119,13\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"100,35,136,85\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"154,37,157,37\"}]"} {"title":"... and the cross-sectional area of the surface on which the force is applied ...","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"160,8,194,53\"}]"} {"title":"... and inversely proportional to the length along which the force is applied.","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"147,75,191,124\"}]"}Review
According to Hooke’s law, which we first encountered in Section 6-5, the force magnitude \(F\) is proportional to the distance \(\Delta{L}\) that the spring stretches, provided that \(\Delta{L}\) is small compared to the relaxed length of the spring, \(L_0\):