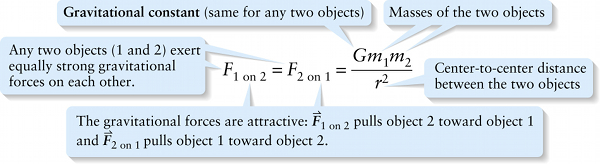
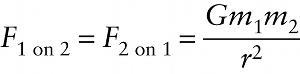Newton's law of universal gravitation (10-2)
Question
Any two objects (1 and 2) exert equally strong gravitational forces on each other.
{"title":"Any two objects (1 and 2) exert equally strong gravitational forces on each other.","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"144,22\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"1,21,17,49\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"100,21,125,48\"}]"} {"title":"The gravitational forces are attractive: vector F sub1 on sub 2 pulls object 2 toward object 1 and vector F sub 2 on sub 1 pulls object 1 toward object 2.","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"18,40,73,59\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"119,41,176,57\"}]"} {"title":"Gravitational constant (same for any two objects)","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"205,2,228,29\"}]"} {"title":"Masses of the two objects","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"228,11,254,30\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"261,11,292,29\"}]"} {"title":"Center-to-center distance between the two objects","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#333333","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"239,52,255,70\"}]"}Review
In both Coulomb’s law (Equation 16-1) and the law of universal gravitation (Equation 10-2), the force that one object exerts on the other is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. In addition, the gravitational force is proportional to the product of the masses of the two particles, while the electric force is proportional to the product of the charges of the two particles. As remarkable as these similarities are, there is one essential difference between the two laws: Newton’s law of universal gravitation tells us that two objects with mass always attract each other, but Coulomb’s law states that two charged objects can attract or repel each other, depending on the sign of the charges they carry.