Chapter 17. Gravitational potential energy (10-4)
Question
/O0qzMt0w2kqxQSPVPihJ/4w4EECKkjrGveUcP76IrCdi+LqCftr3ZB25C4CyPciDkDLeuUdtq0j1czFMc7RxtCvicu6SImA
Question
YAedzCq0ZEOgMZeOeDspHoKP+DmzwlVk7RClNP60f6QuCE/8/krMzPawIDNhzlJk5WntdkR8J0c=
Question
tfDBnh/BepSwtrb1e/2zgz5IuSepnnA6sPKyVRXnm+k=
Question
LMP4MOB8r+d1yzLOdKTbwj8EPGomhMh072hoe+Pt4/SBRA8v+KTdcrL4JifJtIPqbbJ+CaI4CXo=
Question
t7pbmBaYpkR3wSVAxBTknf0gwaNDksIcbrK8eLn6Clm+Qorv7ccRYtdva49jWEOV26OKlHh0NVqoOk/ZcTyYkfL+adLifmJqLI3Oy+FStGQY+rzB0HR+iu8YQebzzVrVj/C1rTnaxAhCcP73ivxnvAwmDfsr+di8L+0hfHFA9iOUkA+JF0wMFx3KLLPZs1WCsEXgsurGh0NP/i2qGtYQd/4F98Pk/Rnug+5qVWaYk3yzrS1iKfXqY+OZksHrxs6DRL+X1ciszCz5m+Hr3SRquVvXRtA8NSKHBzsiekXZI3gSnt8c
Review
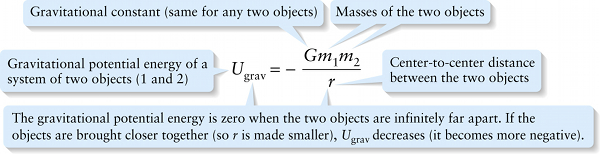
Figure 17-4a graphs the gravitational potential energy given by Equation 10-4. We choose the point at which potential energy \(U_{\mathrm{grav}}\) is zero to be where the two objects are infinitely far apart, so \(r \to \infty\). The gravitational potential energy is negative for any finite value of \(r\) and increases—that is, becomes less negative—as the objects move farther apart. That’s because the work done by the gravitational force and the change in gravitational potential energy are negatives of each other: \(\Delta{U}_{\mathrm{grav}} = -W_{\mathrm{grav}}\) (see Equation 6-16 at the beginning of this chapter section). If we hold object \(m_1\) stationary and move object \(m_2\) farther away, increasing the distance \(r\), the attractive gravitational force does negative work. Then \(W_{\mathrm{grav}} < 0\), so \(\Delta{U}_{\mathrm{grav}} > 0\) and the gravitational potential energy increases, as Figure 17-4a shows.