Acceleration as a function of time for simple harmonic motion (12-15)
Question 1 of 4
Question
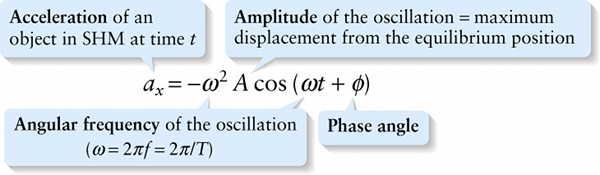
\(\textbf{Acceleration}\) of an object in SHM at time \(t\)
{"title":"Acceleration of an object in SHM at time t","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"9,10,24,30\"}]"} {"title":"Amplitude of the oscillation = maximum displacement from the equilibrium position","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"118,11,119,13\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"100,7,117,30\"}]"} {"title":"Phase angle","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"113,132\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"195,33,199,34\"},{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"132,99\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"217,8,232,34\"}]"} {"title":"Angular frequency of the oscillation (ω = 2πf = 2π/T)","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"167,12,186,29\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"67,10,90,30\"}]"}Review
So for an object in simple harmonic motion the value of the phase angle \(\phi\) tells you the point in the oscillation cycle that corresponds to \(t = 0\). Note that Figures 12-6a and 12-6b really depict the same oscillation, with the same amplitude \(A\) and period \(T\); the only difference is the point in the cycle that we call \(t = 0\).
The phase angle also appears in the expressions for velocity and acceleration in simple harmonic motion (Equations 12-7 and 12-8), which we found by analogy with uniform circular motion: