Chapter 14. Rate of energy flow in radiation (14-22)
Question
cTbDGUTFpMGXQdeVjPN7M3zQG++CFyvaOQZy85cAXYKdBzW0FSrSN7KZ9PJwYvFX68DaTD9TvxJSg+94LXYMeF1prAs=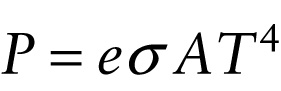
Question
9NgC0aJE77hUOPss0YDzU/7pF6/jA2p0w42ZpKaVH1ZlFnv3N9hZKh/LeA+qpavJsNaySM1PFLo=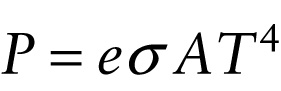
Question
/QJm3I04bkKwZ/+/6aD72hDxf08y/oVgEi2B2+9+u8RyH4rZDAr1v3MXdoR4fVIoBCk0zQ==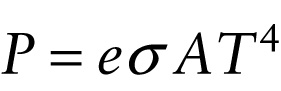
Question
MitZt1jrCOdhTSU/h+Y41AgZjCGeK3uAXOlJV80Ul10=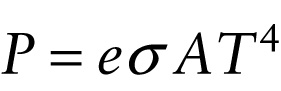
Question
r22ZAyeScUQbgk7yW27sRjhGuWzOLSLTUC5ZE3JaDeqjNRVtRkgjo9rfhizldBD5rfjPSq5p/T3Ua0S/GRAMQFPwcEJ3sEzkaObW4BS5/aHkrCRcuFCF2KUpc/UbJAHt4nmw0it/gsf55fKMAhifM2gCsjE=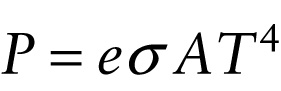
Review
Experiment shows that any object emits energy in the form of radiation. The rate at which radiation is emitted by an object—that is, the radiated power \(P\) in joules per second or watts—is proportional to the object’s surface area \(A\) and to the fourth power of the Kelvin temperature \(T\) of the object:
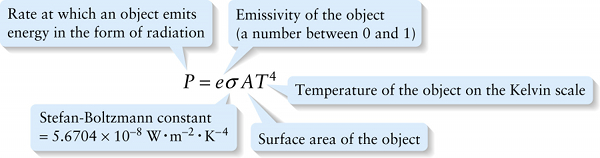
The Stefan-Boltzmann constant \(\sigma\) (the Greek letter sigma) has the same value for all objects. The quantity \(e\) is the emissivity of the surface; its value indicates how well or how poorly a surface radiates. A surface with a value of \(e\) close to 1 is a good radiator of thermal energy.