Chapter 26. Rate of energy flow in radiation (14-22)
Question
hord1rEI1KB3aDnLBgoFL5sGNaw7wOJyj2aHRJ0RH982THBMIAOxsXf2hydwHQmSe13DHBge+3a0PEBooTnlRR6uGMKSdeWL7tVRy22LK52epNTL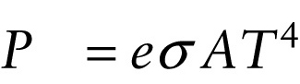
Question
qWhqClIXXFjUjplQ2U+4j7de8yeHsxe6q8Ud0wdHhwk6RlXNZjrkpsQAYwxp6j1KsFlSU40iAvDsSmwWBRo7W0+i5mRQWxIH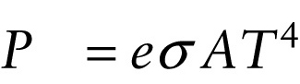
Question
jCqq48UbK6Uz+S856Y8EkJ37av0hKKXEoiEnY/PE+HH/OEOxbtNy5Gxgxn1VlI/LTObhdgT3tS1Ghk01u7guj7qjfIc=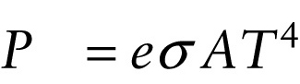
Question
atT93OssX3/lNqqa74iYm7xqrniTRoj95OmxAg44QsY=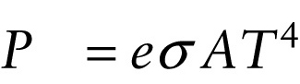
Question
CWAvCJM/hBvtg8fCBmufv2e4/B52W63BBnlK8GGyrXWglw6qd/bxNMURt0exHO62eJWw6ICQWM5P3LlsTuWlfJ3fYP10L+XcdE8G1mHt/2OQoyRA/vpFl8BMXWlvSQymNUIibCgQkemGYLOxKseAHhtiTg5bL3YpB8rayw==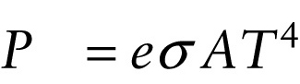
Review
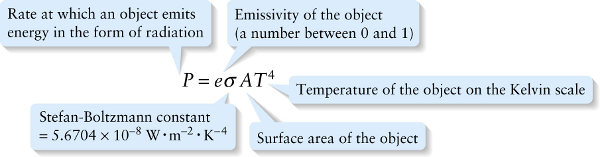
The higher the temperature of an object of a given size, the greater the radiated power \(P\) and so the more brightly it glows.
Experiment also shows that the color of the radiation emitted by an object depends on its temperature \(T\) (Figure 26-4). A heated object emits light at all wavelengths, but emits most strongly at a particular frequency called the frequency of maximum emission. As the temperature increases, the frequency of maximum emission increases.
Equation 14-22 shows that the radiated power also depends on a quantity \(e\) called the emissivity, which depends on the properties of the object’s surface. This has its greatest value \((e = 1)\) for an idealized type of dense object called a blackbody. An ideal blackbody does not reflect any light at all, but absorbs all radiation falling on it.