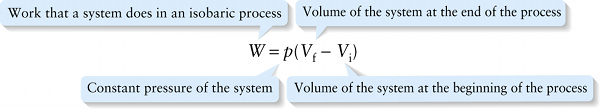
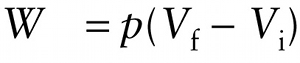Work done in an isobaric (constant-pressure) process (15-4)
Question 1 of 4
Question
Constant pressure of the system
{"title":"Work that a system does in an isobaric process","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"4,2,50,42\"}]"} {"title":"Volume of the system at the end of the process","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"161,1,204,57\"}]"} {"title":"Volume of the system at the beginning of the process","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"240,0,289,56\"}]"} {"title":"Constant pressure of the system","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"117,13,146,51\"}]"}Review
The volume of a cylinder is equal to the area of its base multiplied by its height. So \(A\ell_{\mathrm{i}}\) and \(A\ell_{\mathrm{f}}\) are, respectively, the initial volume \(V_{\mathrm{i}}\) and final volume \(V_{\mathrm{f}}\) occupied by the gas, and we can rewrite Equation 15-3 as
(15-1) \(\ \ \ \ Q = \Delta{U} + W\)
It’s conventional to rearrange this equation with \(\Delta{U}\) on one side and \(Q\) and \(W\) on the other side: