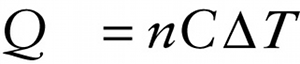Quantity of heat and the resulting temperature change in terms of molar specific heat (15-10)
Question 1 of 4
Question
Number of moles present of the substance
{"title":"Quantity of heat that flows into (if Q > 0) or out of (if Q < 0) an object","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#99CCFF","code":"[{\"shape\":\"poly\",\"coords\":\"82,133\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"10,16,12,16\"},{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"4,9,48,62\"}]"} {"title":"Molar specific heat of the substance of which the object is made","description":"Wrong","type":"incorrect","color":"#ffcc00","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"179,5,217,51\"}]"} {"title":"Temperature change of the object that results from the heat flow","description":"Incorrect","type":"incorrect","color":"#333300","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"259,2,300,55\"}]"} {"title":"Number of moles present of the substance","description":"Correct!","type":"correct","color":"#000080","code":"[{\"shape\":\"rect\",\"coords\":\"144,19,177,51\"}]"}Review
In Equation 14-20 the quantity \(c\) is the specific heat of the substance. For an ideal gas we usually write the internal energy \(U\) in terms of the number of moles of gas present rather than the amount of mass. We follow the same approach for the quantity of heat \(Q\), so we write
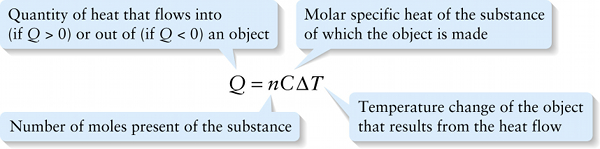
The quantity \(C\) in Equation 15-10 is called the molar specific heat of the substance (in the case we're discussing, an ideal gas). It has units of joules per mole per kelvin or \(\mathrm{J}\ /\ (\mathrm{mol}\cdot\mathrm{K})\).