Chapter 15. Pressure and volume for ideal gas, adiabatic process (15-22)
Question
x2Aw8cTdg4DX6RytWWea4tpa2EhYSr0rjhuRRQ==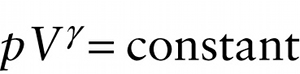
Question
cyXXO0Z4umbYNPxdrDpqPRCfRgD4uMbWm6X3+A==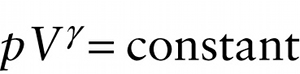
Question
vMpEZmhc9HPucj1royvNz2hezzz1OkQf/tqnyzD+u//uI+tz4q4+GGwdYSGEs7KTDvs0m+cL97E=
Question
6KgCeGOYweLI51ymeNtnej5OjQK3sS0YGuVf8QMtVvspPN2c47MAVZGF9kgTsOHcsPpqImb85nG2j/85rf5tMztoR3e0J+rJDFkTTi0YDXWSxZ54KrxTENoWULWsTwUewK5p3dq4bR8VzXu6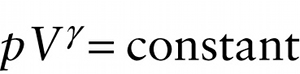
Review
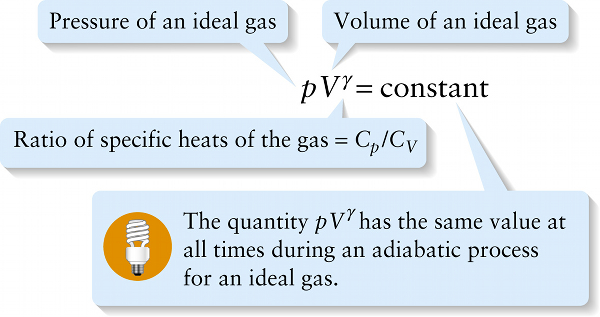
The ratio of specific heats \(\gamma = C_p\ /\ C_V\) for an ideal gas plays an important role in adiabatic processes in which there is zero heat flow into or out of the gas. If we have a quantity of gas in a cylinder with a moveable piston and then allow the piston to move in or out, the gas will compress or expand adiabatically if the cylinder and piston are made of an insulating material that does not allow heat to flow through it. It can be shown that if an ideal gas expands or contracts adiabatically, the pressure \(p\) and volume \(V\) of the gas are related by